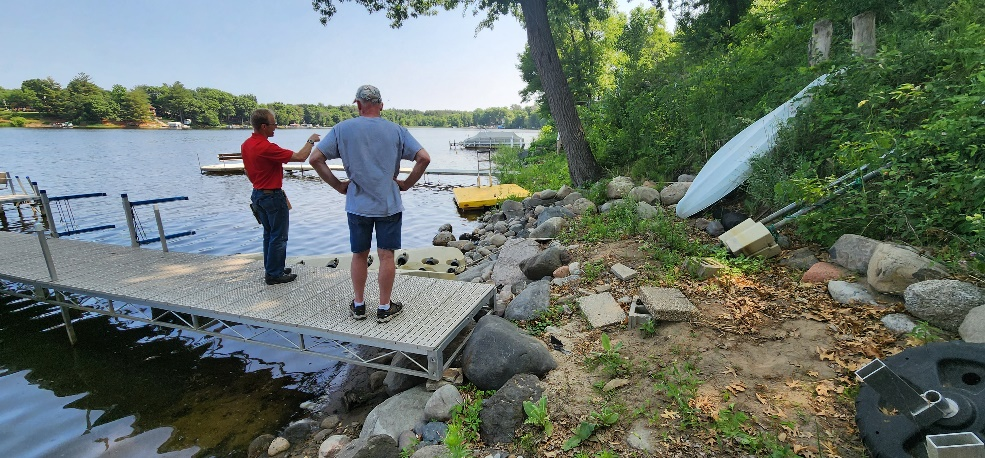
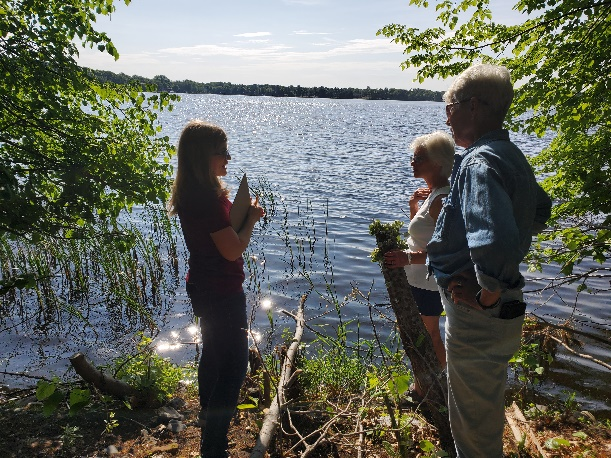
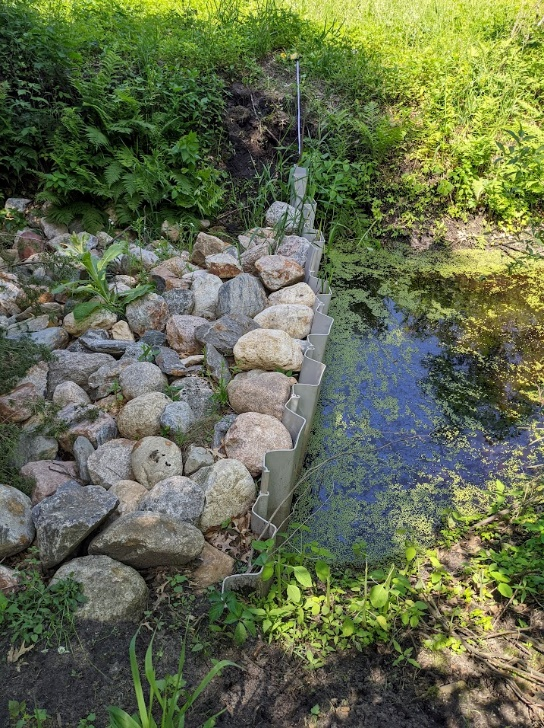
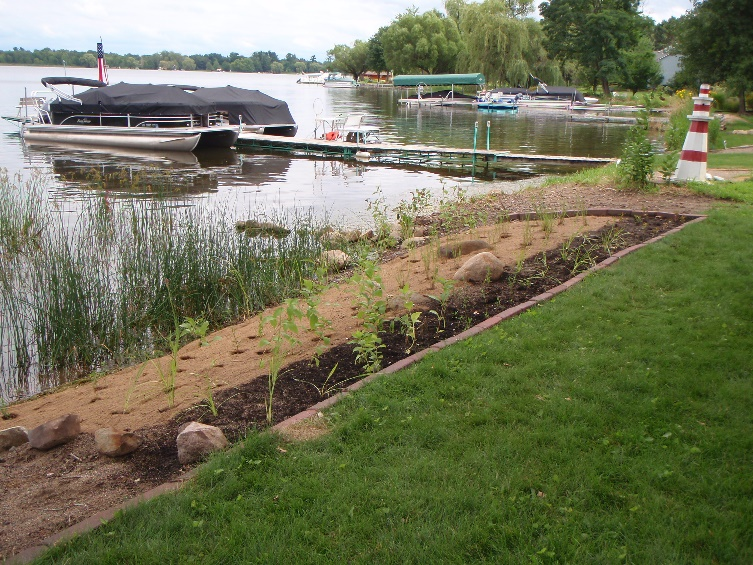
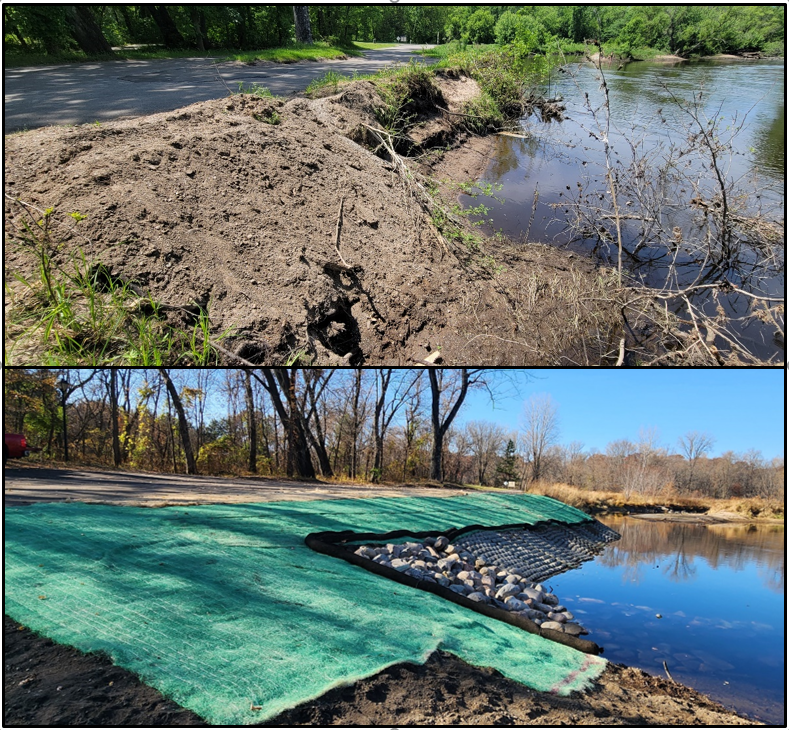
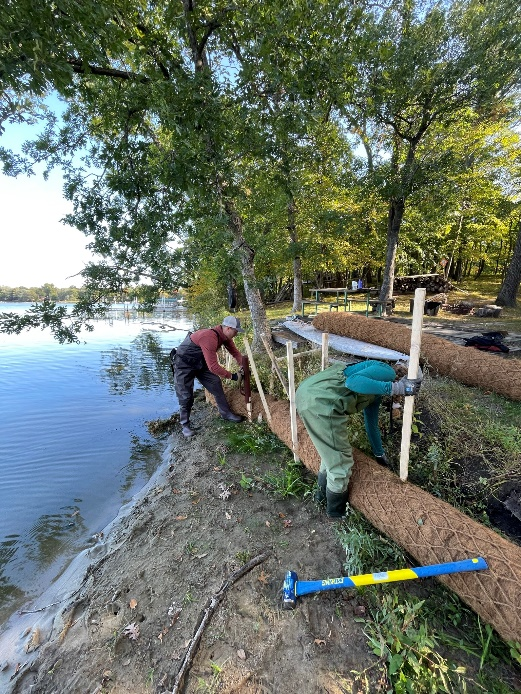
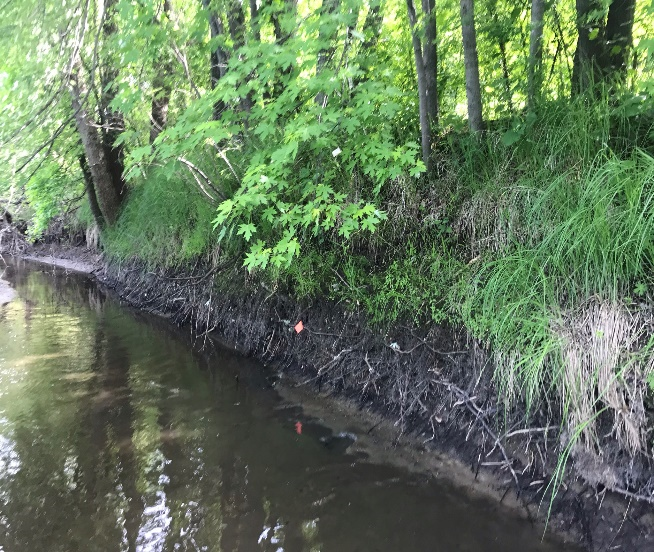
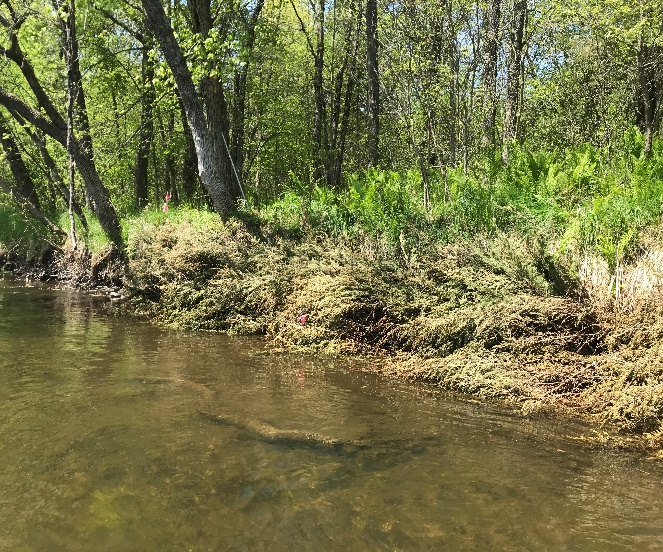
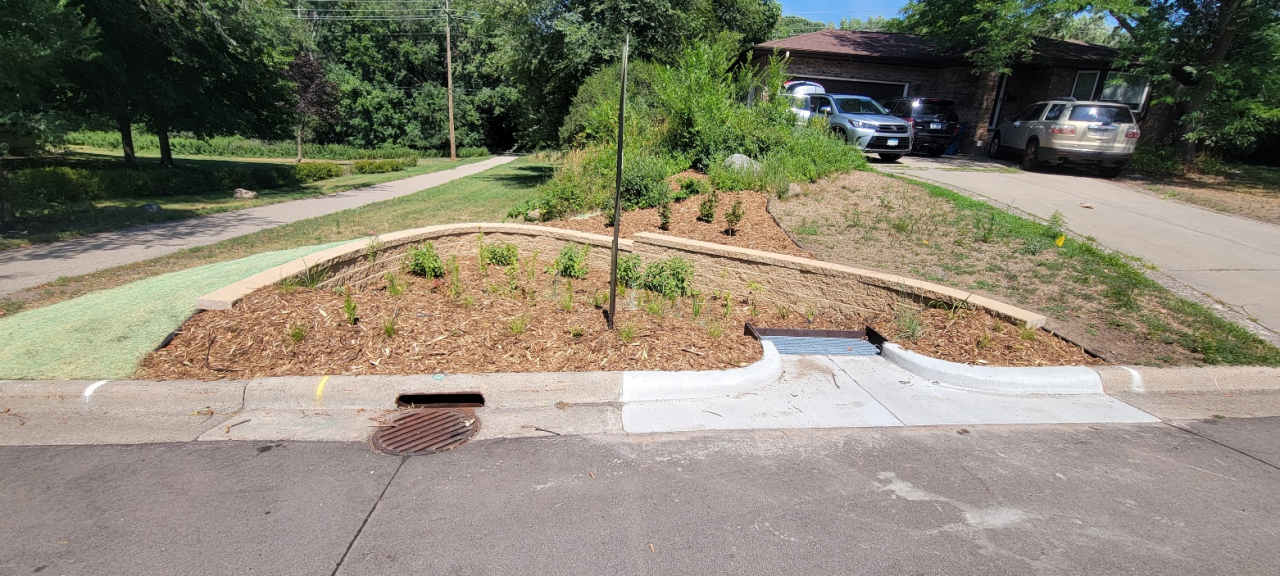
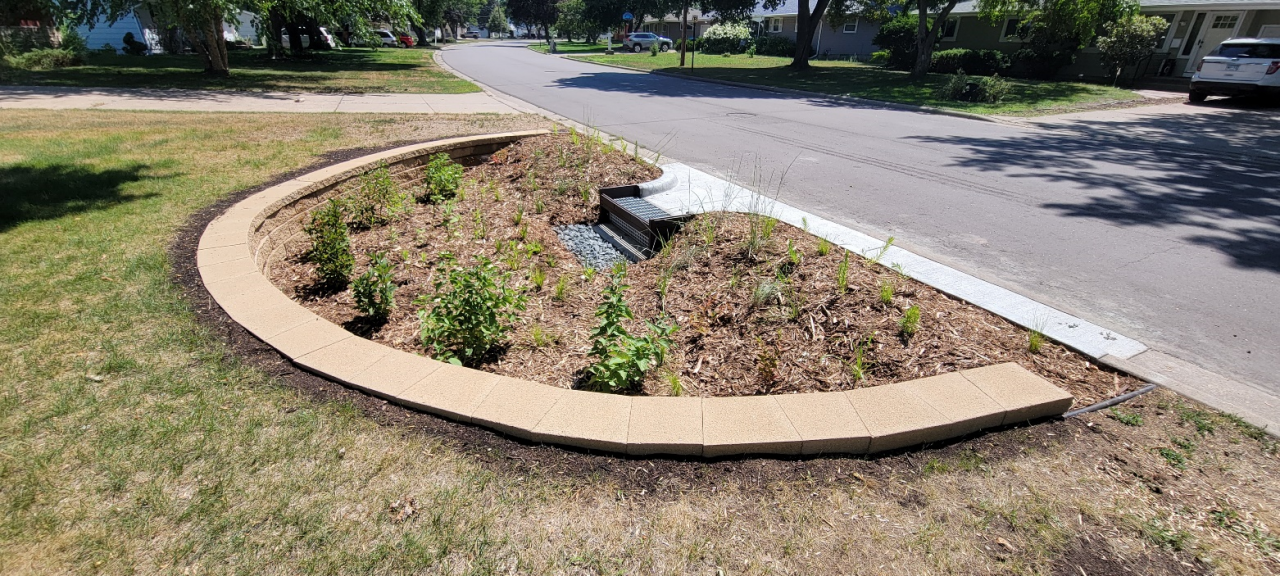
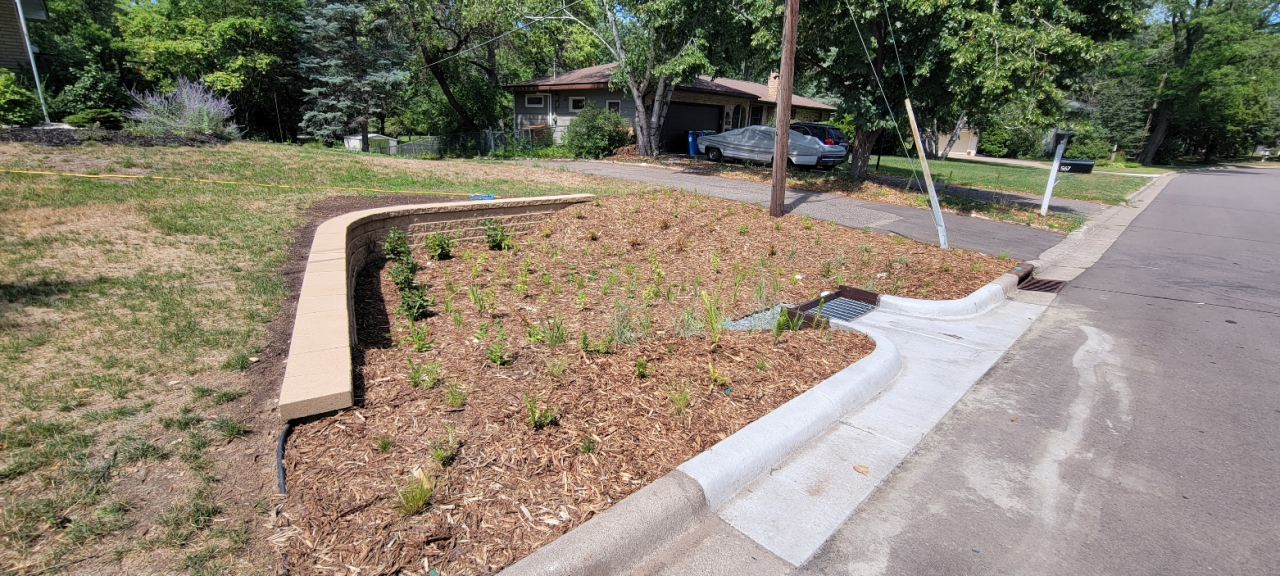
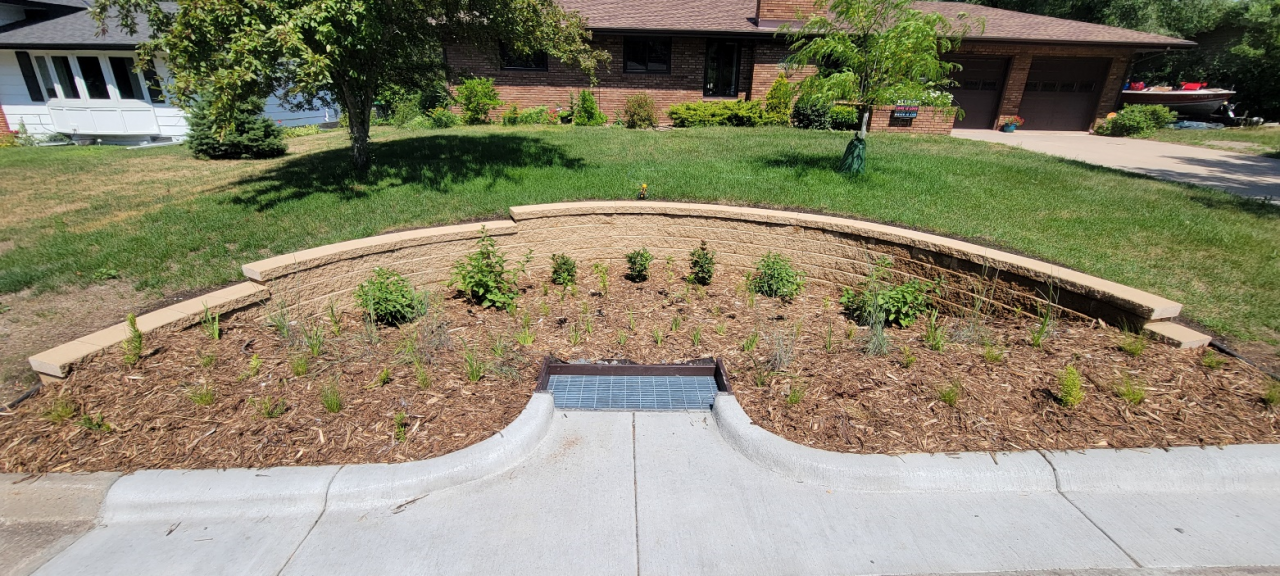
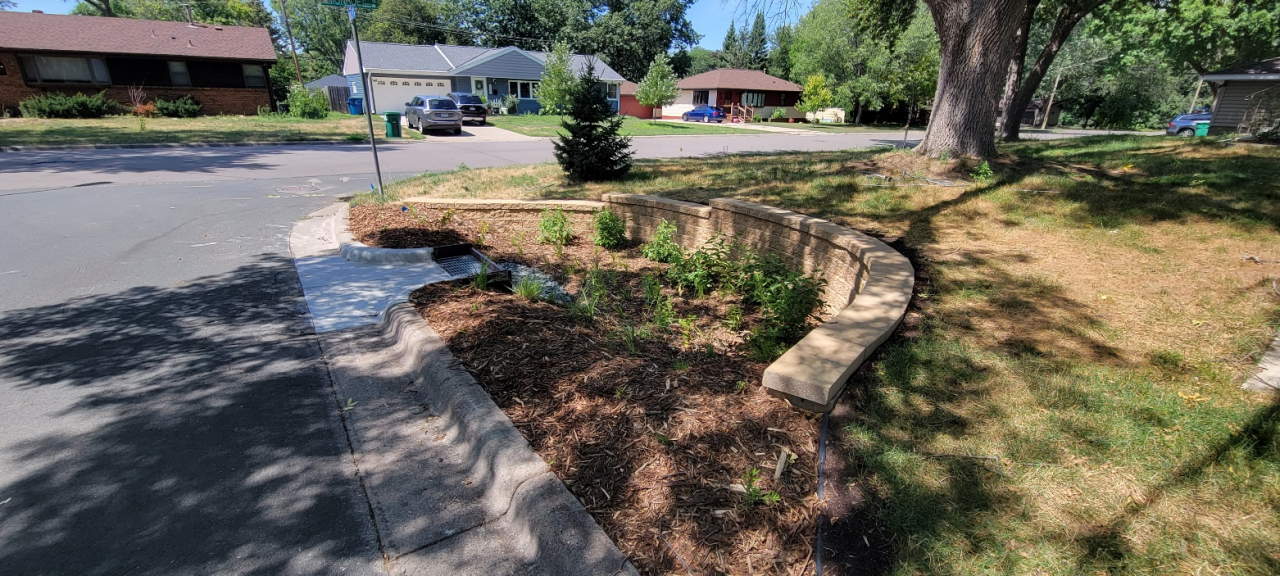
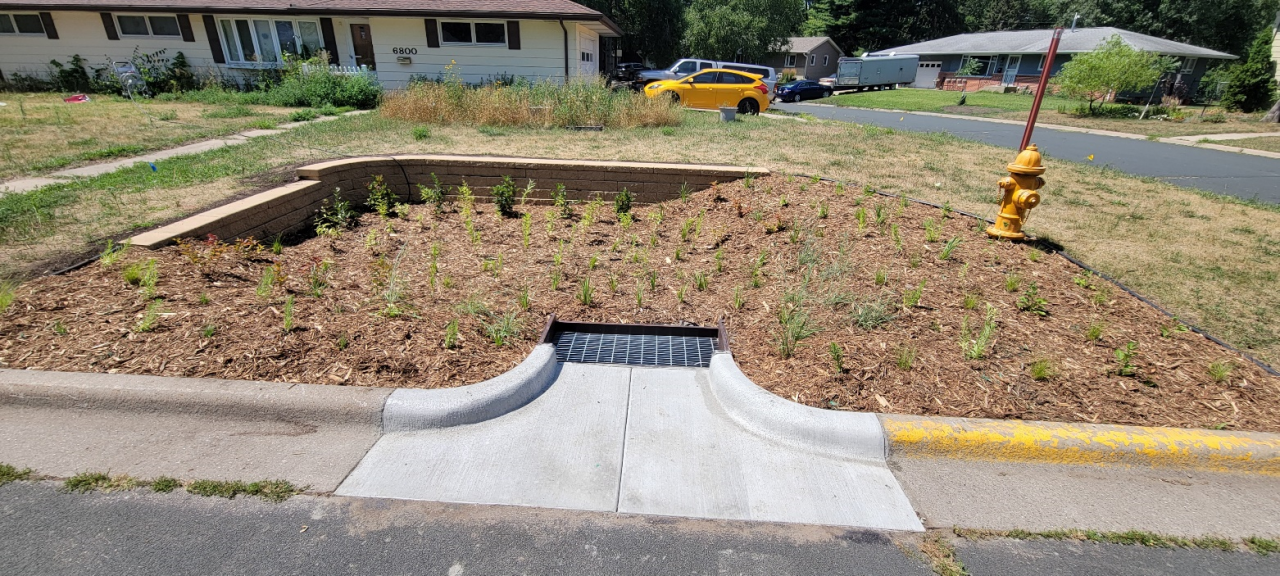
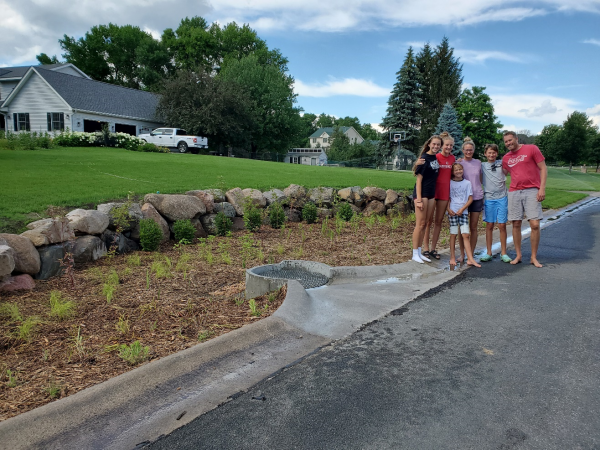
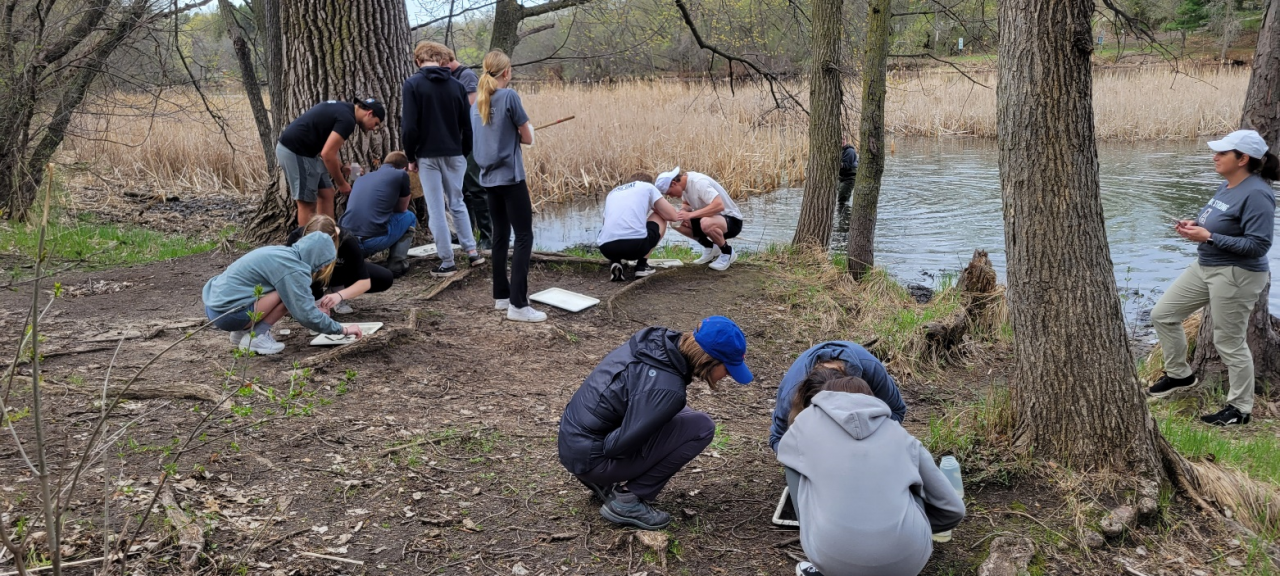
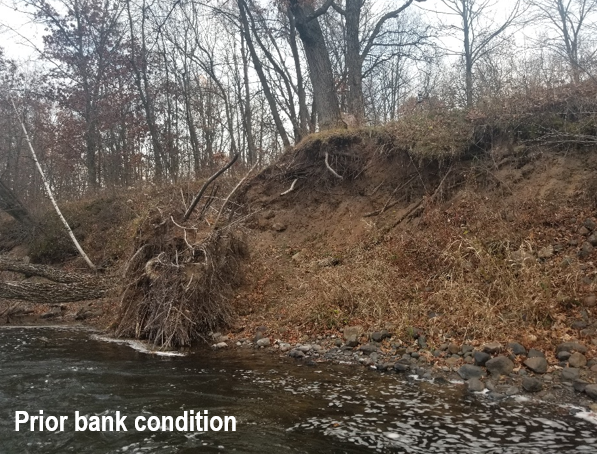
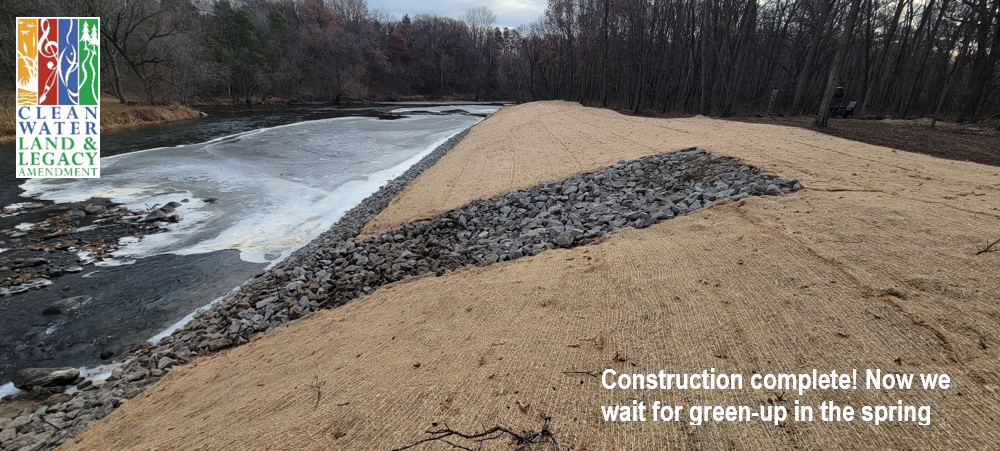
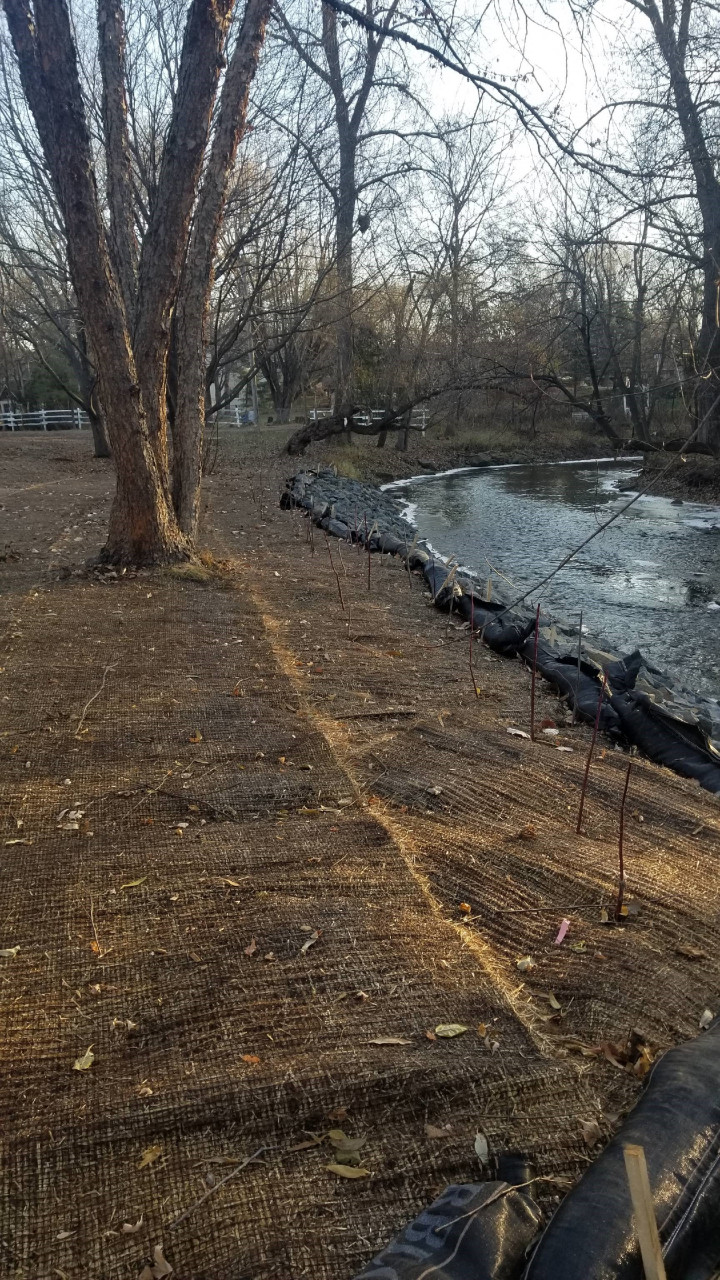
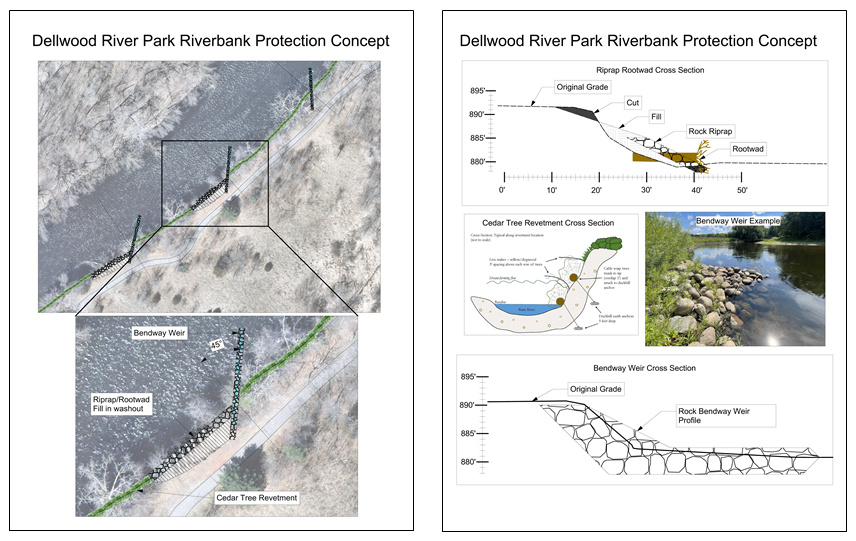
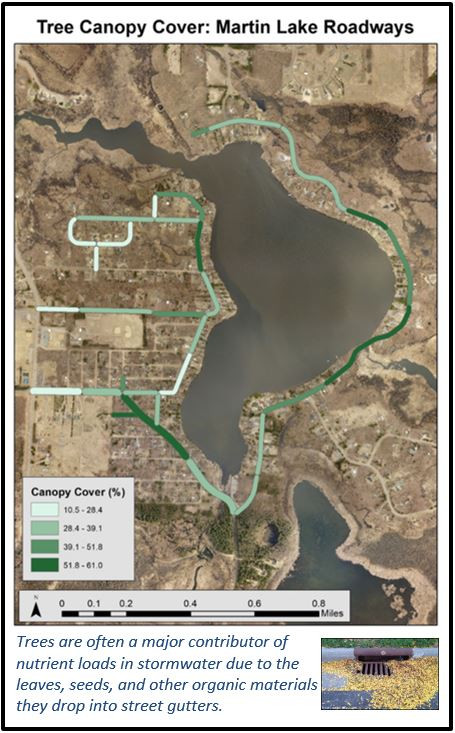
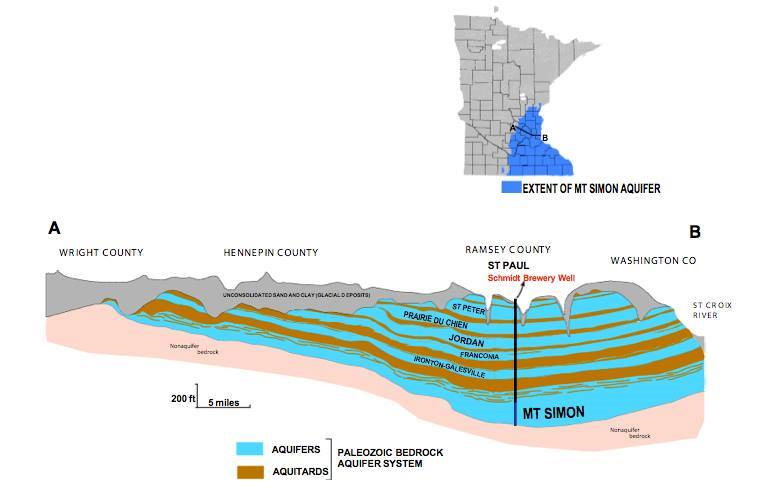
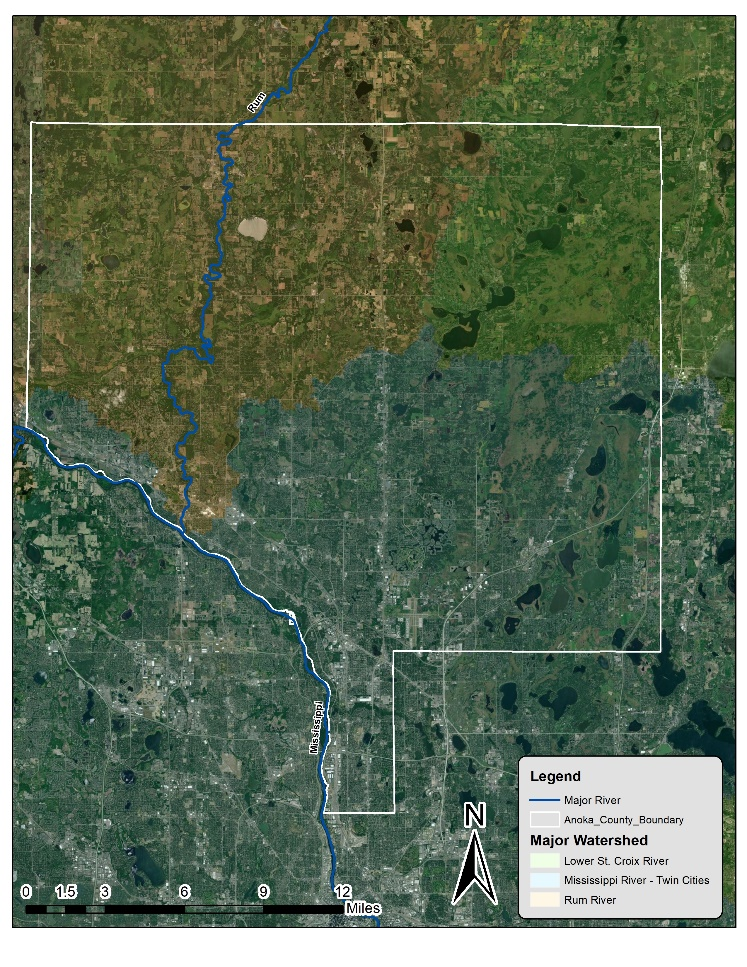
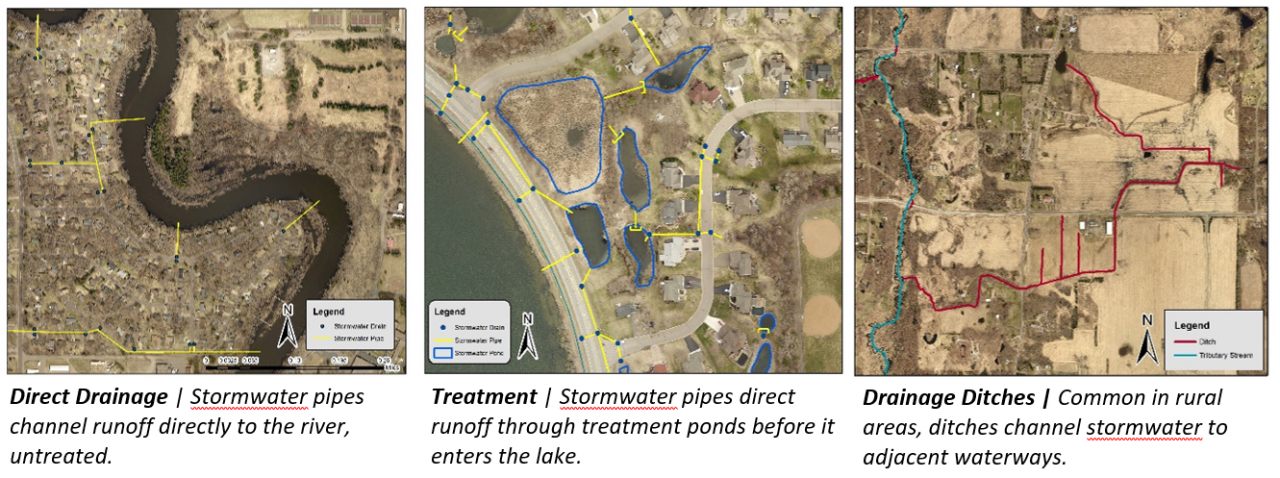
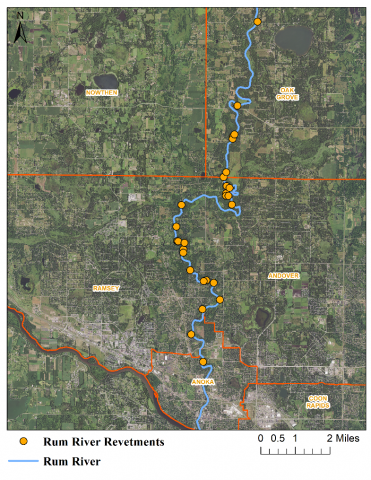
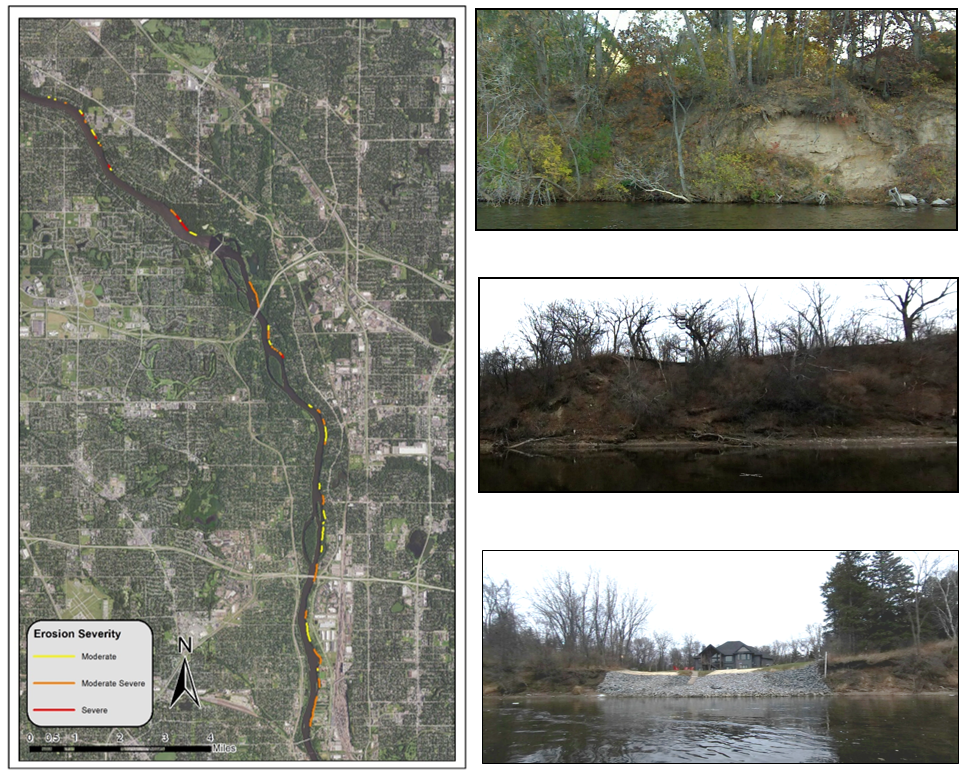
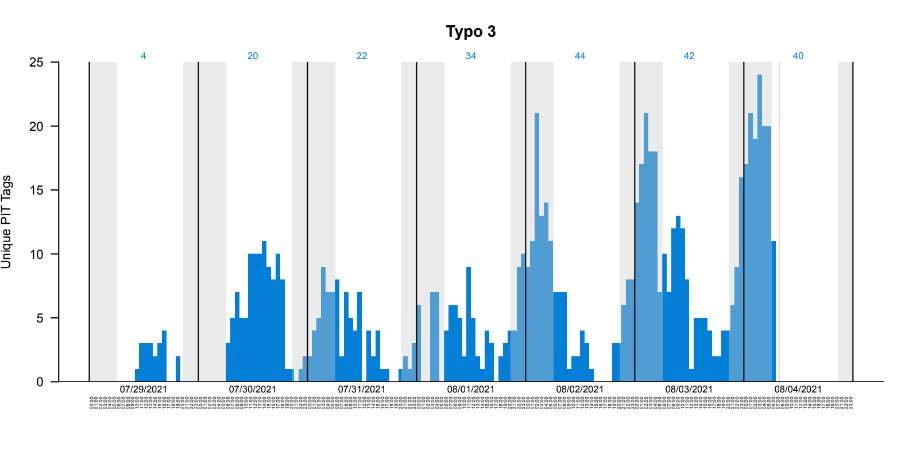
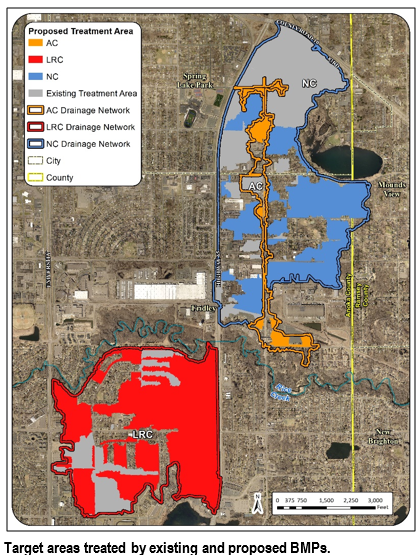
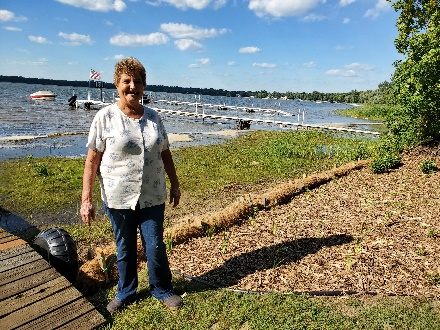Six curb-cut rain gardens were installed approximately one-year ago and have been capturing runoff and its associated pollutants ever since. With each rainfall, runoff flowing in the street gutter is redirected into the rain gardens via a cut in the curb. Following a rain event, the water that enters the rain gardens is able to soak into the ground, which better mimics the natural hydrology before impervious surfaces (e.g. roofs, driveways, roads, etc.) and storm sewers directed runoff directly to Rice Creek. The rain gardens are able to store water and are filled with native species that were carefully selected for the site-specific conditions (e.g. light, soil type, and moisture).
Cumulatively, the six rain gardens are estimated to infiltrate 455,000 gallons of water, as well as remove 605 pounds of sediment and two pounds of phosphorus loading to Rice Creek annually. The native plants help to maximize infiltration and provide the co-benefit of pollinator habitat. One additional rain garden is located adjacent to a trail entrance into Locke County Park, providing an excellent public education opportunity.
These rain gardens were installed in partnership with the landowners, the City of Fridley, and the Rice Creek Watershed District. ACD provided design services and construction oversight.
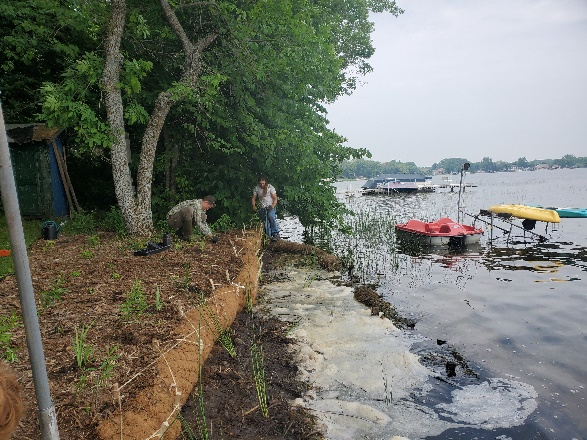
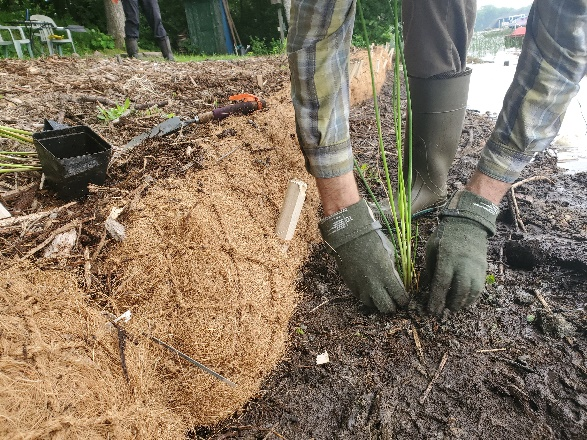
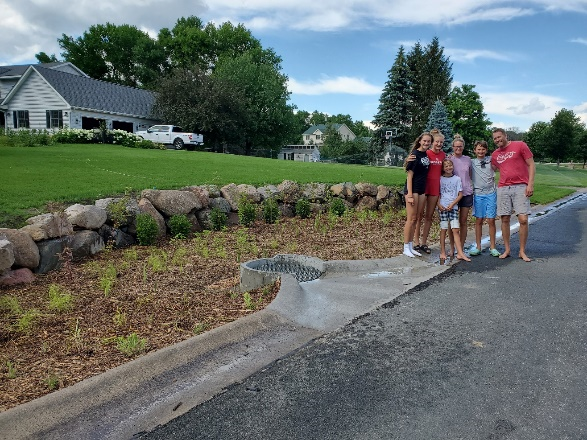
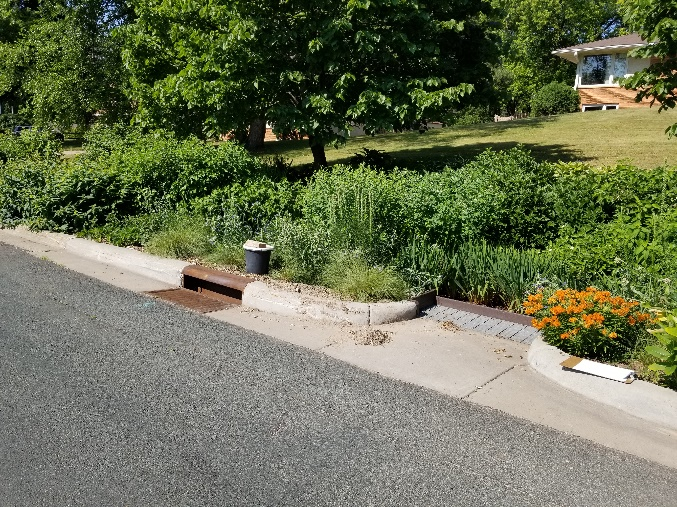
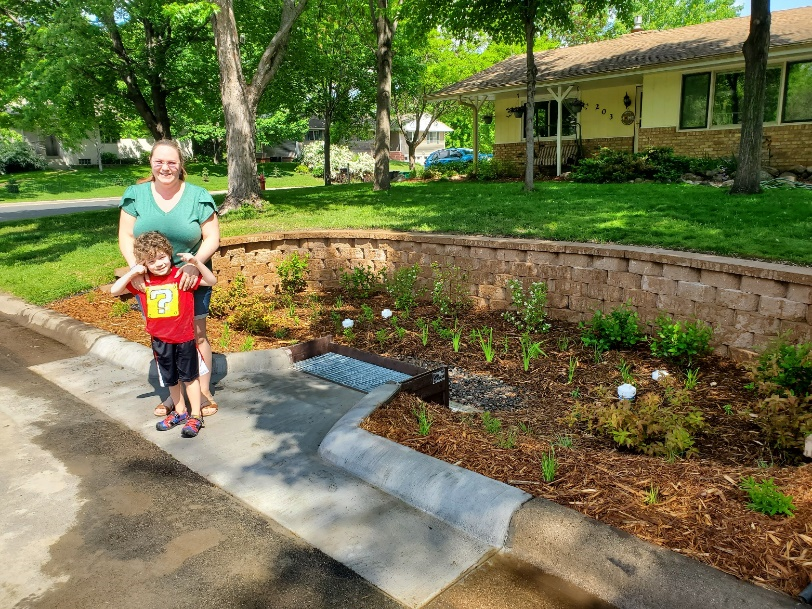
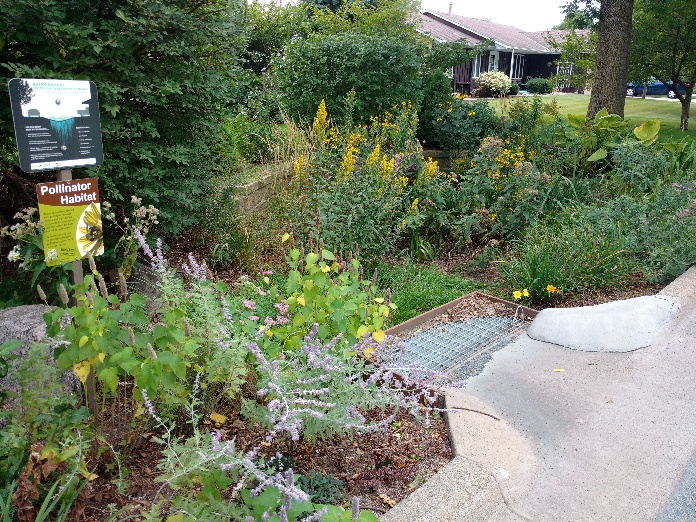
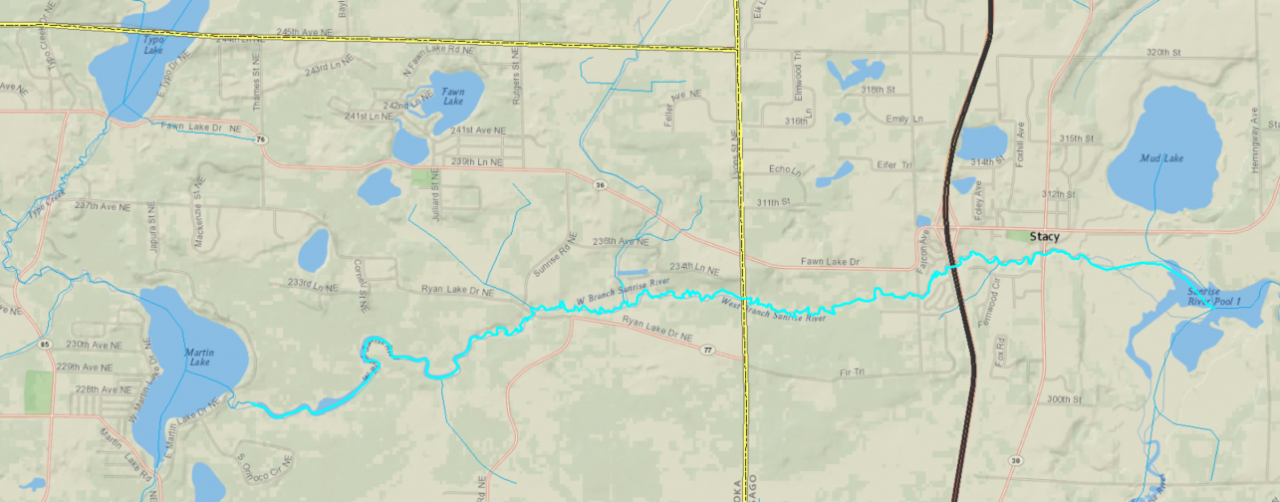
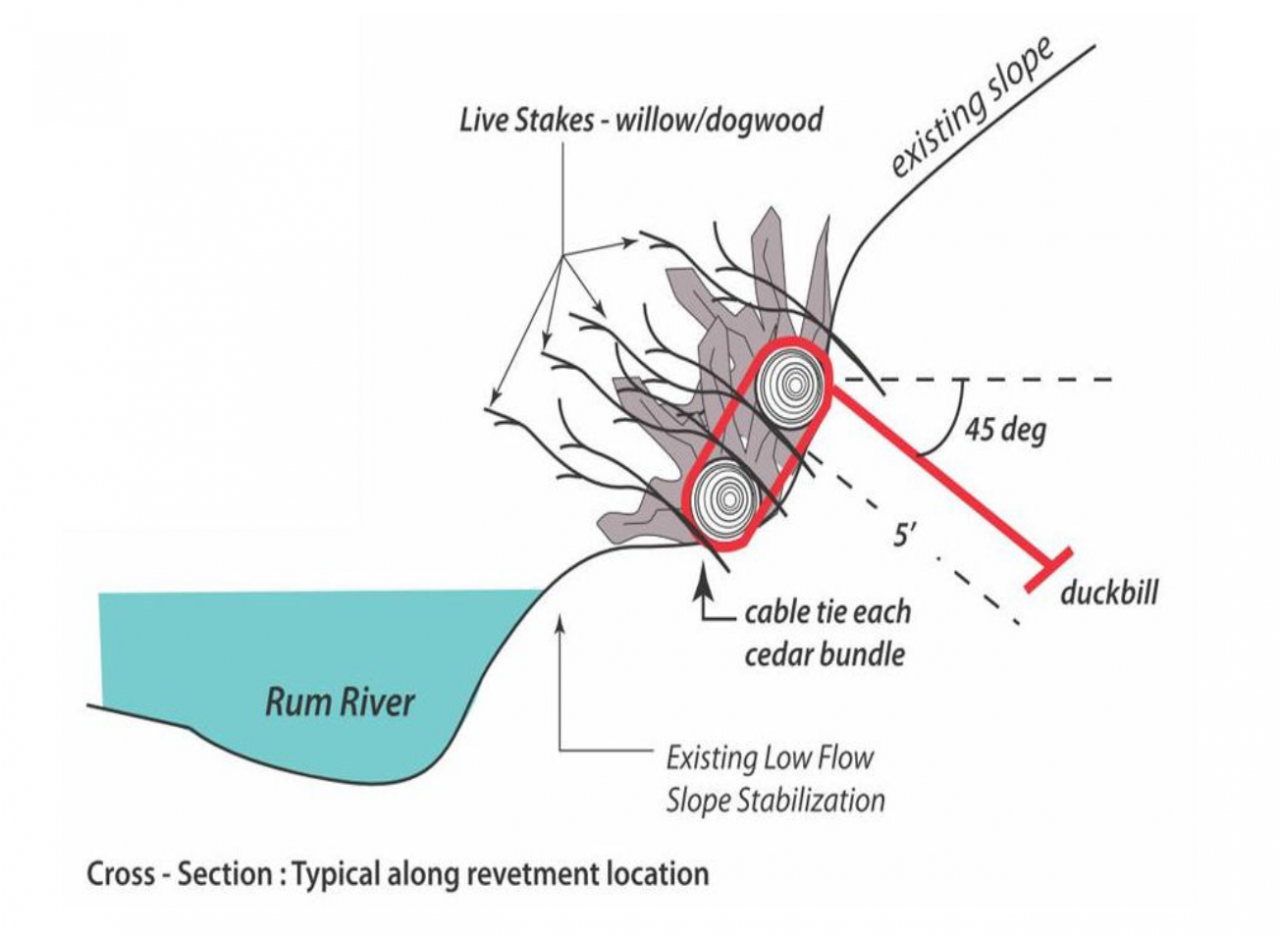
The rain garden shown in the pictures below was planted last summer and as you can see, it didn't look like much at the time. Now, it looks beautiful and is full of flowers which pollinators love! This rain garden captures curbside runoff from 6.5 acres of neighborhood which previously went untreated to the Rum River. The native plant's roots create channels through the soil and reduce compaction, ensuring a maximum amount of water can infiltrate into the ground. The homeowners who worked with ACD to make this rain garden a reality, kept weeds at bay, and provided irrigation for the new plants during drought conditions!
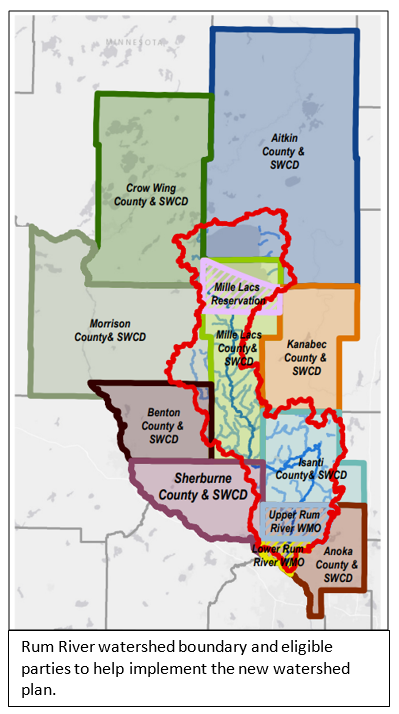
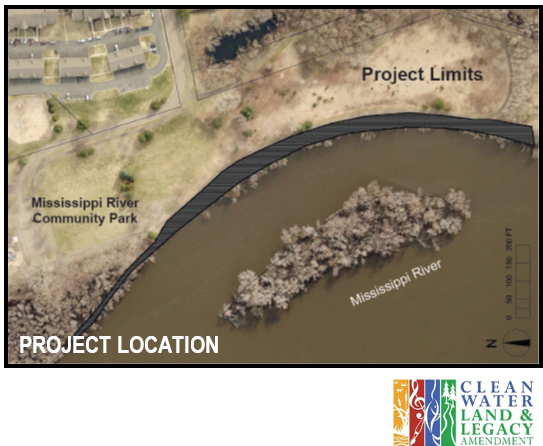
Project funding was from the Clean Water, Land, and Legacy amendment, and the Lower Rum River Watershed Management Organization. To see other rain gardens installed throughout Anoka County, please see the virtual project tour on ACD's website.
For more information on rain gardens in Anoka County contact Mitch Haustein at