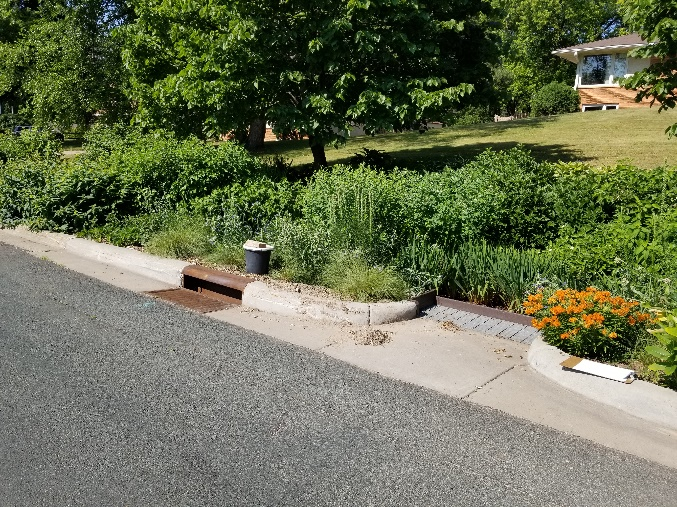
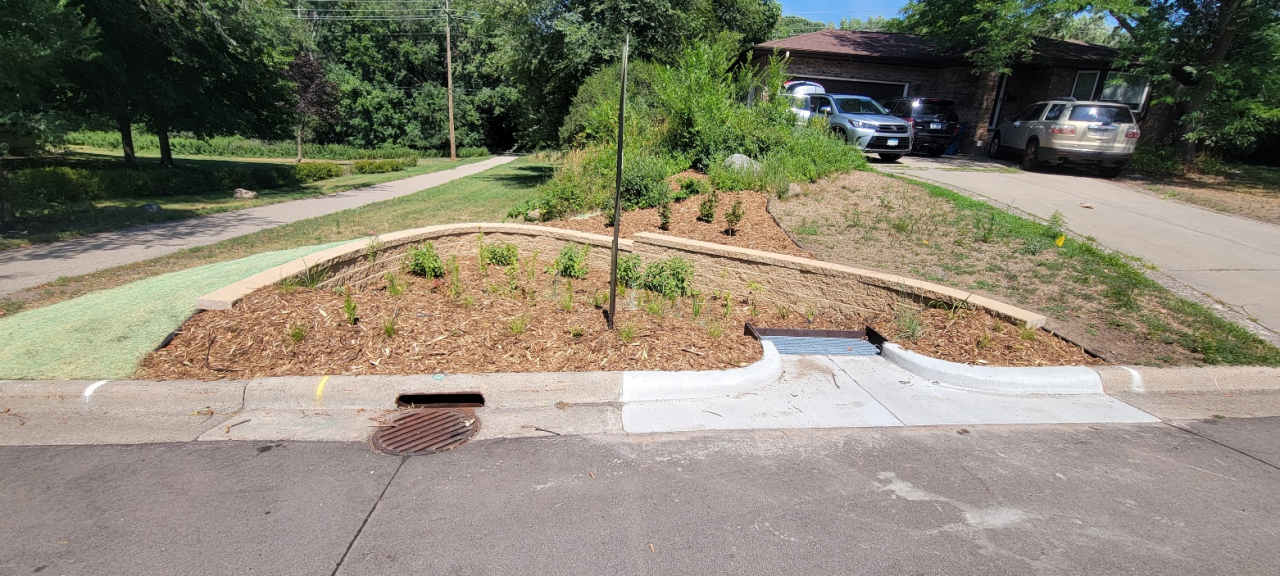
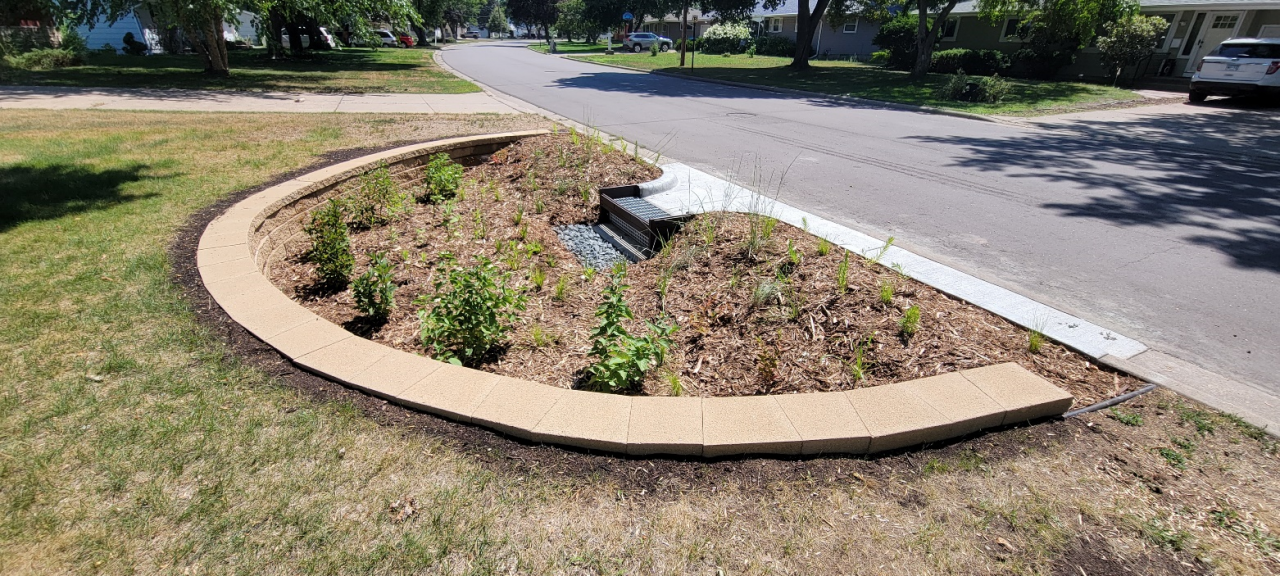
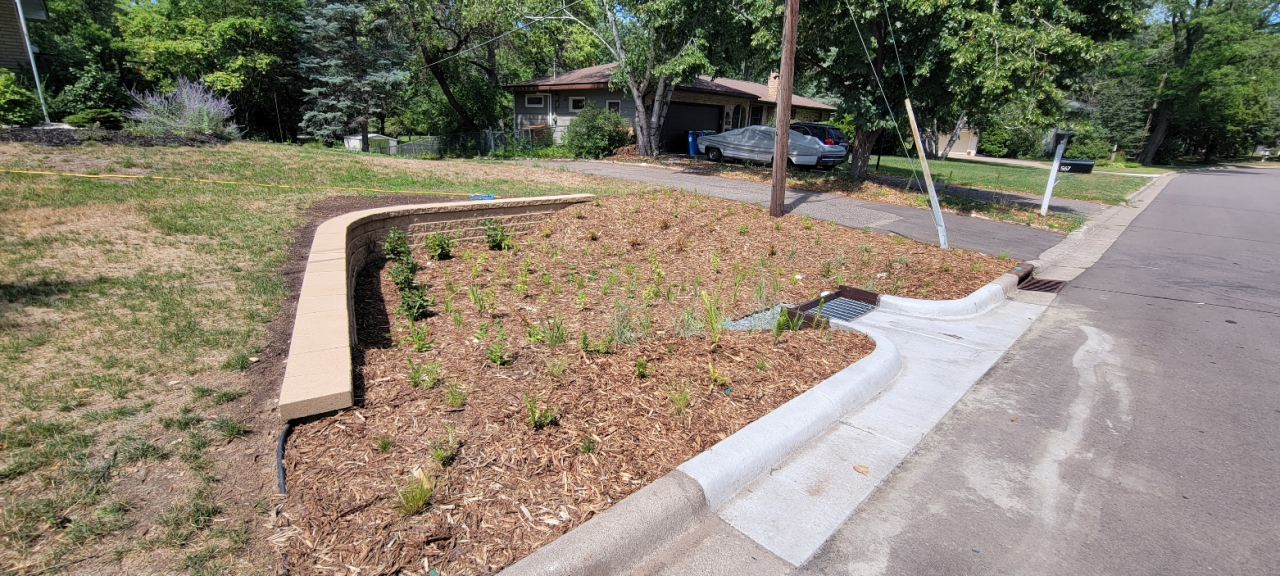
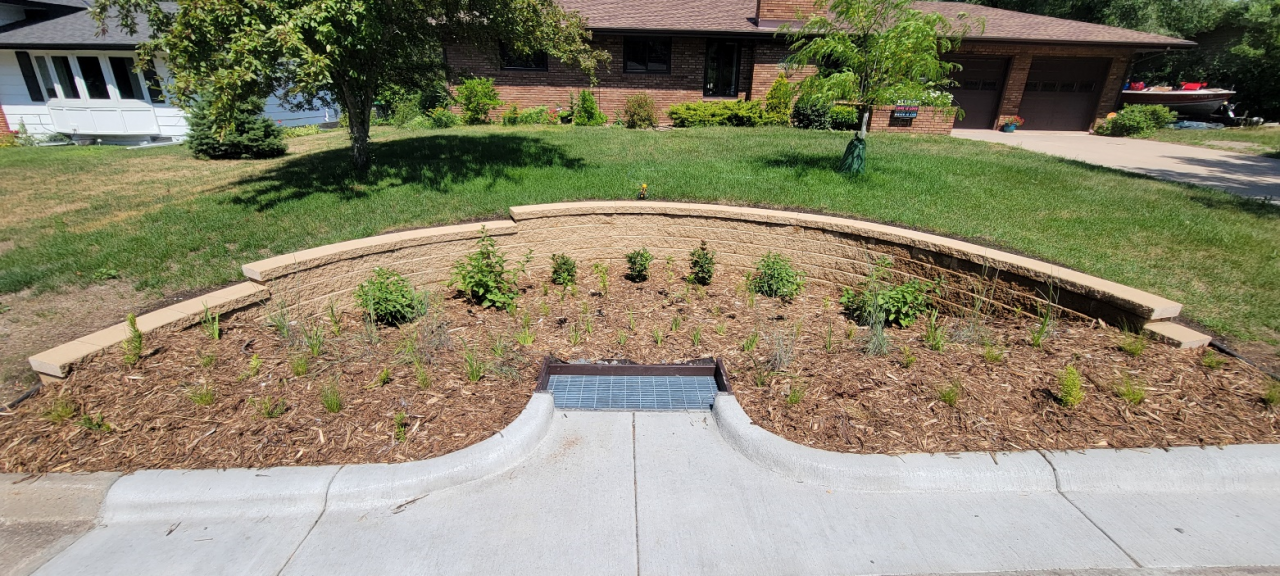
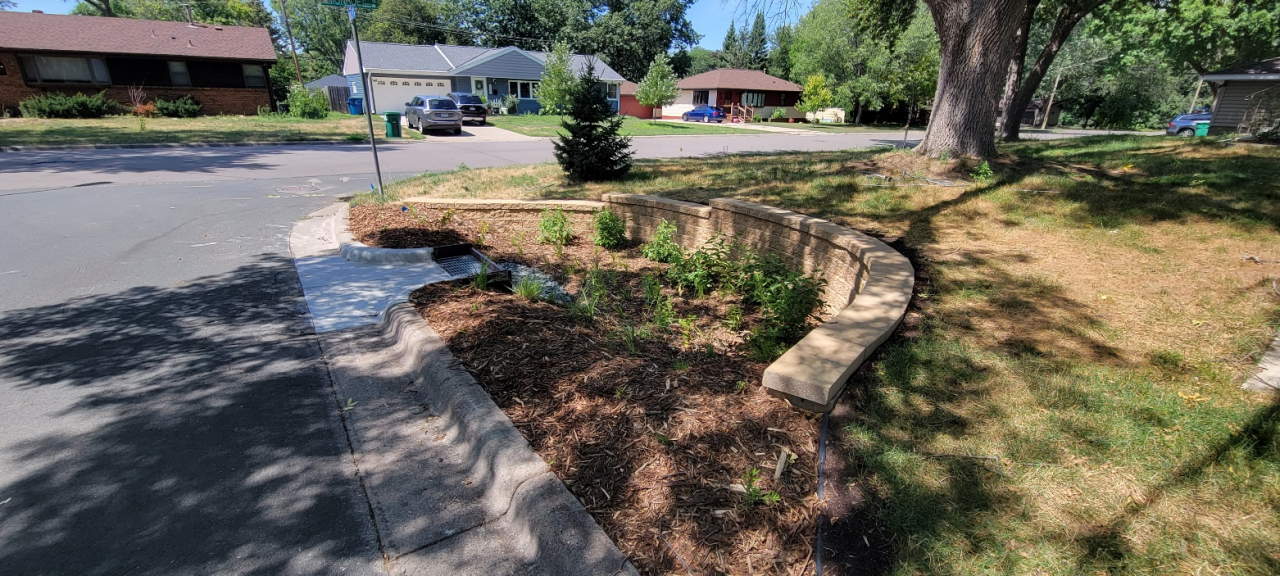
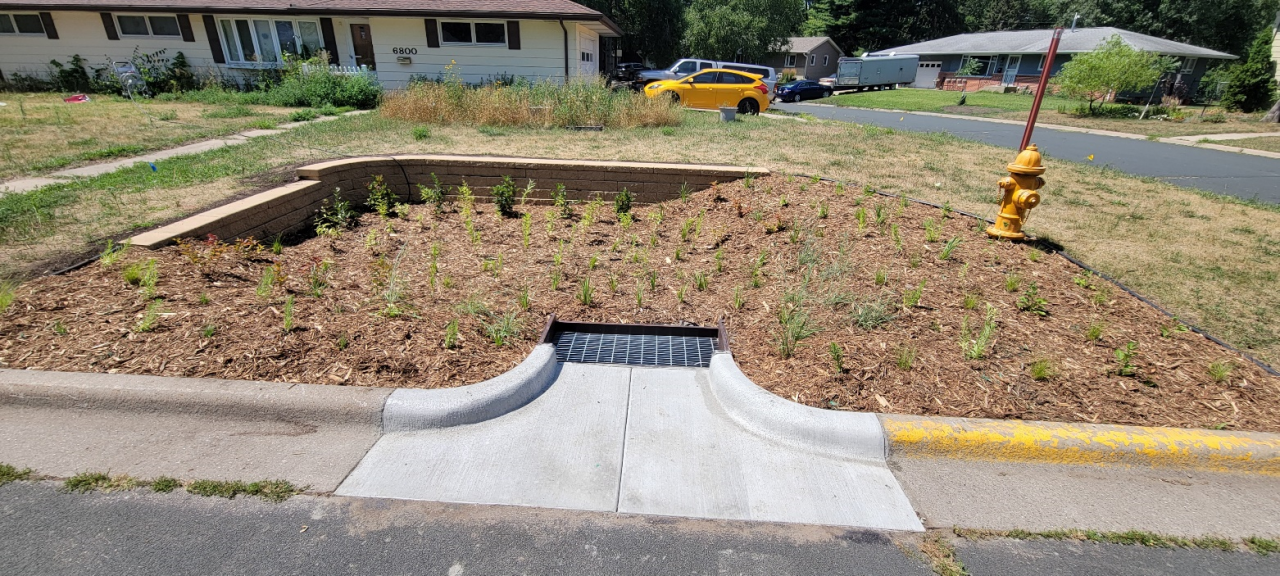
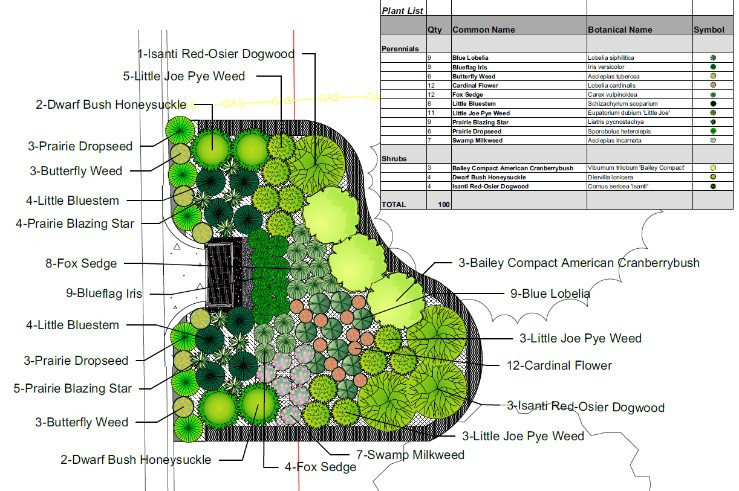
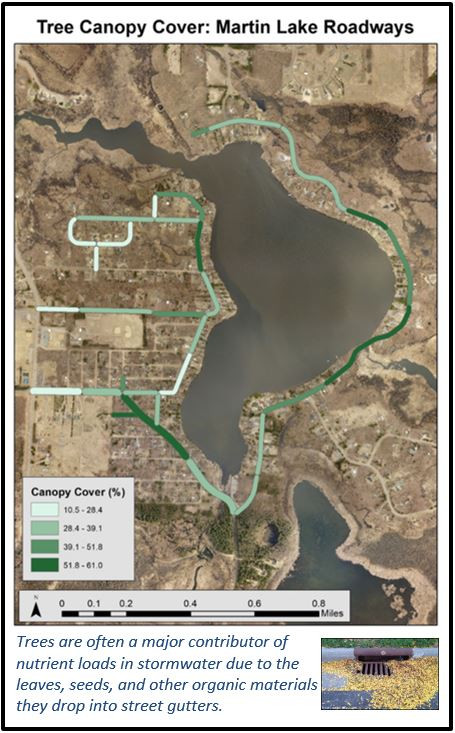
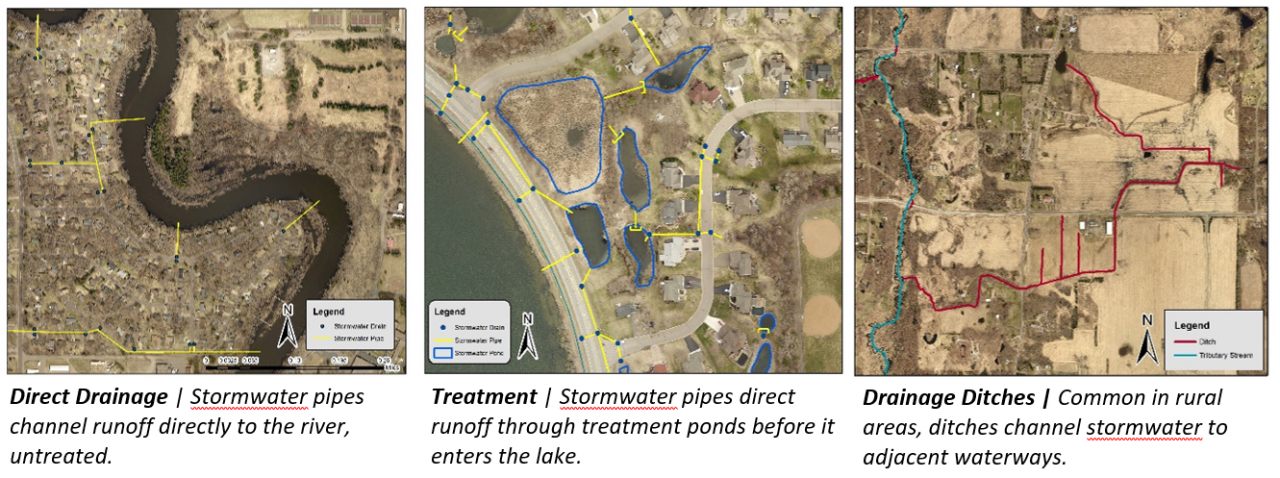
Unlike our sanitary sewers, water, trash, and other debris entering storm drains are not routed to a treatment facility; instead, they drain into wetlands, lakes, and rivers. Some stormwater pipes drain directly to these waterbodies, while others may first pass through features like manmade ponds to provide some treatment. In either case, reducing pollution at the source is the most effective way to protect our local waters. To this end, the need to keep trash and debris out of the streets is clear. However, when flushed down the storm drain, even organic plant materials such as grass clippings, leaves, and other yard waste also contribute to harmful nutrient pollution, causing algae blooms, reduced oxygen levels, and other issues in downstream waters.
Keeping excess plant material out of the street isn't just beneficial for water quality; it also prevents flooding, reduces the cost of storm sewer maintenance and repair, and improves travel safety. It's for these reasons that intentionally blowing leaves, grass clippings, or other materials into the street is illegal in most Minnesota cities. Instead, dispose of them at your local compost facility or through a curbside yard waste provider. If you'd like to play a more active role in improving stormwater quality, consider becoming involved in the Adopt-a-Drain program. For more information contact Breanna Keith, Water Resource Specialist, at