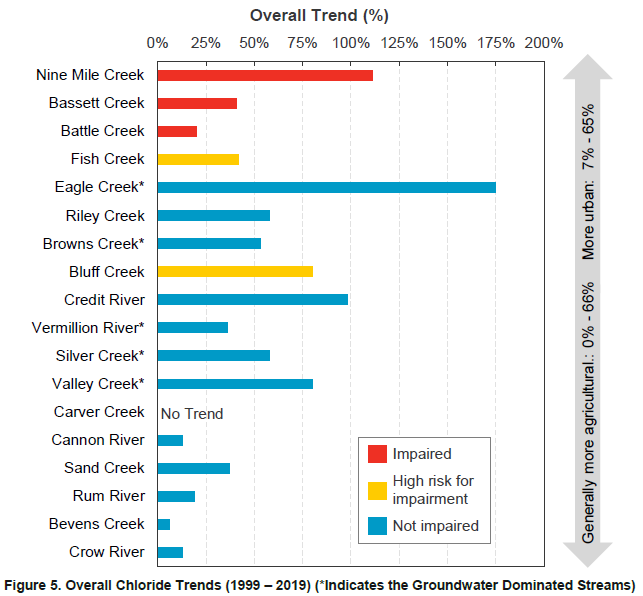
That's how much chloride is released into the environment annually in Minnesota. The biggest sources (in order) are road deicing salts, synthetic fertilizer, and household water softening. Perhaps it should be no surprise we find them increasing in essentially all Twin Cities streams and rivers.
A just-released study from the Metropolitan Council shows increasing chlorides in 18 Twin Cities streams and rivers they monitored. They looked at data from 1999-2019, including data collected by the Anoka Conservation District. Of 18 streams, 17 have a trend of increasing chlorides. Locally, our Rum River has that trend but thankfully low chloride concentrations so far compared to other streams. Chloride tends to be highest in areas with the highest road density.
A few tips to reduce deicing salt and still have good footing:
- Shovel first.
- Use the right amount. Salt works most efficiently (for chemistry reasons) with ~2 inches between salt granules. That means 12 oz. covers a 20 foot driveway or 10 sidewalk squares.
- Don't salt below 15 degrees. Sodium chloride doesn't work below that temperature.
See the full Metropolitan Council report at https://metrocouncil.org/Wastewater-Water/Services/Water-Quality-Management/Water-Monitoring-Pubs/2022-Chloride-Report.aspx