The Rum River is one of the largest rivers in Anoka County, second only to the mighty Mississippi. It starts at the outlet of Mille Lacs Lake and winds through the landscapes of Mille Lacs, Isanti, and Anoka Counties until it discharges to the Mississippi River in the City of Anoka—but many don't know about the progress this river has made to become one of Minnesota's most outstanding waterways.
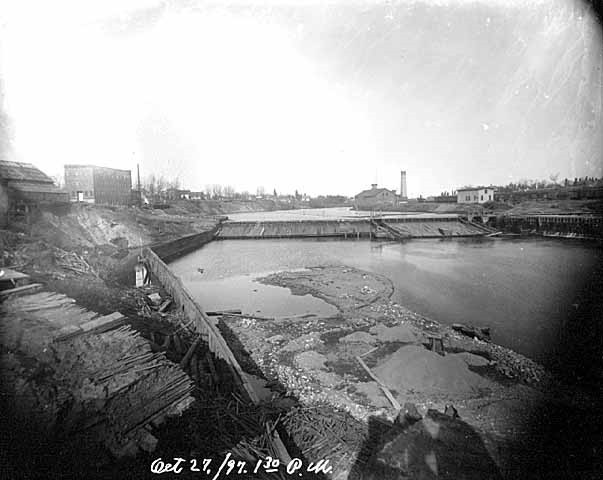
To really appreciate the Rum River today, it's good to understand a bit of its history. For many decades, the Rum River served as a large scale aquatic conveyor for lumber. Large white pine, elm, oak, cherry, and maple all floated down the river from central Minnesota forests to build the homes and business of the growing Twin Cities Metro Area. It also conveyed our sewage, agricultural waste, sediment laden runoff, and industrial by-products downstream to the Mississippi River, and eventually the Gulf of Mexico.
A former Anoka County commissioner who grew up in the area once said that when he was a kid, no one would dare to even fish in the Rum River, much less swim in it. I'm happy to say, over the last 80 years, the fate of the Rum River has been wholly reversed. Today the Rum River is:
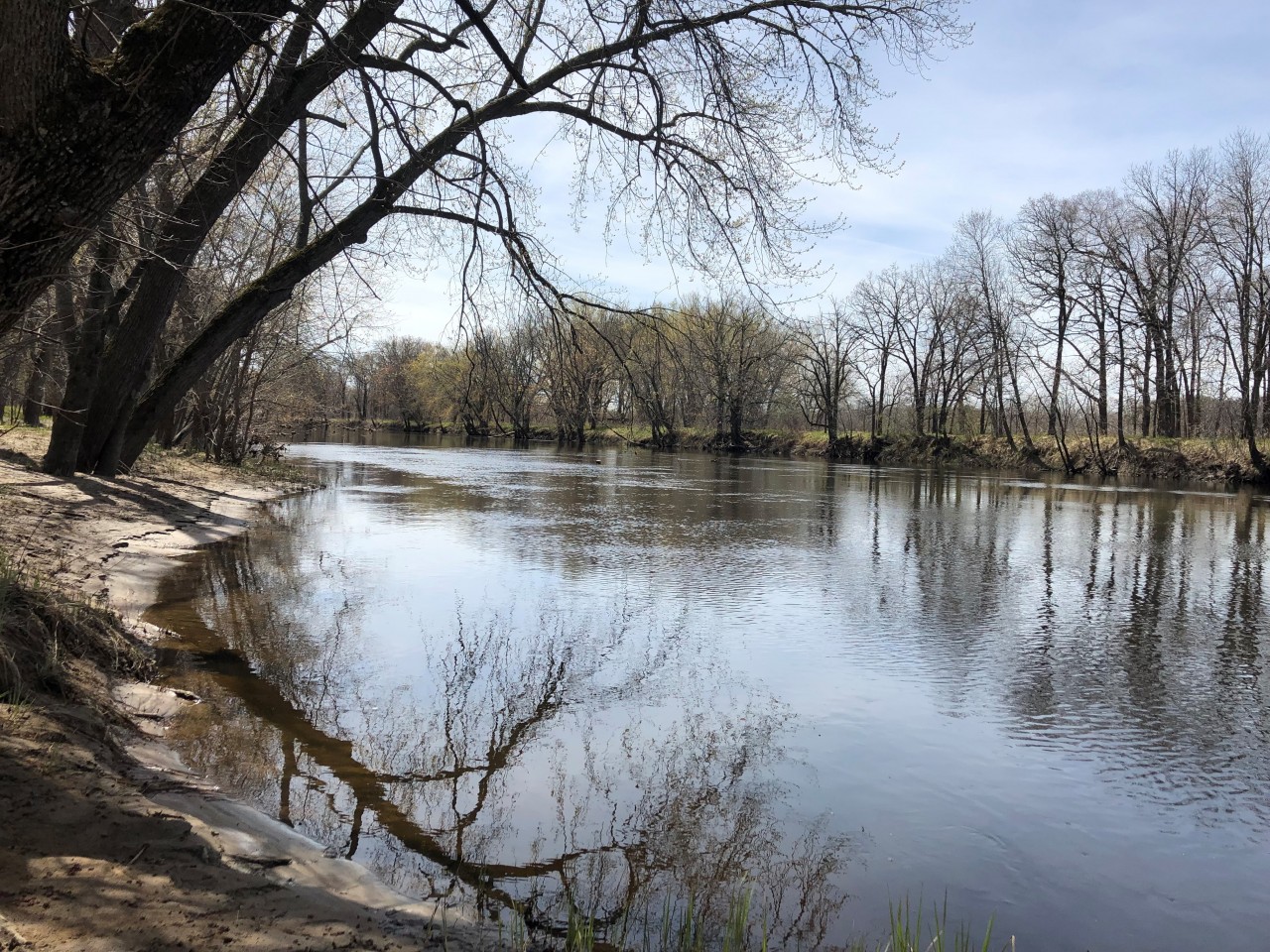
Martin's Landing on the Rum River
- One of 6 Wild and Scenic Rivers and 35 State Water Trails in Minnesota
- Designated as an Outstanding Resource Value Water
- An excellent fishery and waterfowl corridor with abundant smallmouth bass and wood duck
- Key reach for Species in Greatest Conservation Need
This isn't to say that our Rum River is in the clear. In the last 30 years, the population in the area draining to the Rum River has increased by 47%. With that many people came more roads, parking lots, and roof tops that added 74% more stormwater runoff. The increased water volume and speed that came with this extra stormwater caused the river to slice deeper into the landscape and rip apart the riverbanks. When riverbanks collapse into the river, the resulting sediment smothers the fish, amphibians, and reptiles that now call the river home. The Rum River is also increasingly threatened by road salt and nutrient pollution coming from this stormwater.
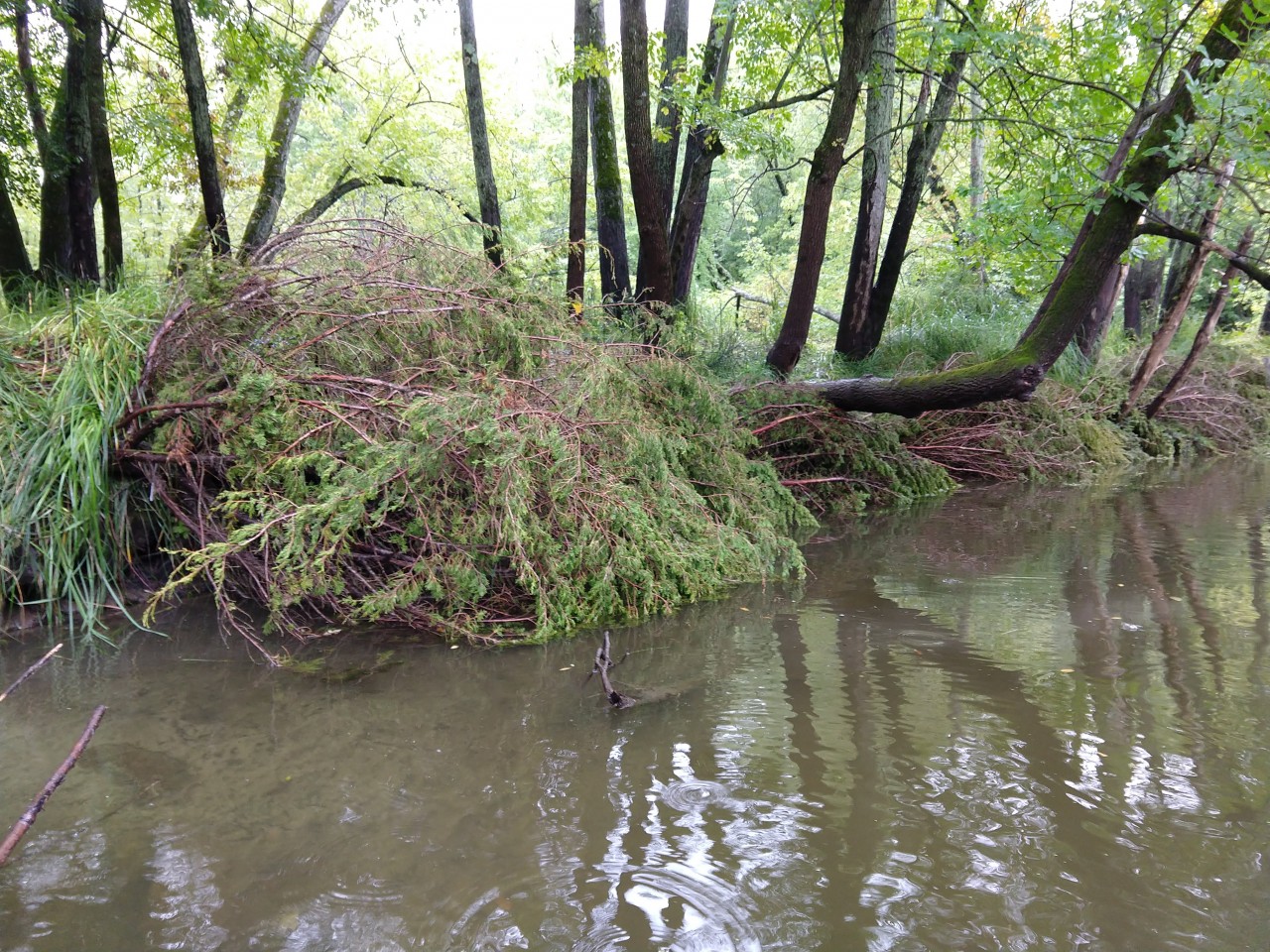
A Cedar Tree Revetment installed to stabilize a bank on the Rum River.
ACD takes a holistic approach to managing these new challenges to the quality of the Rum River. We are heavily involved with monitoring the chemistry and biological quality of the River; we assist the local Watershed Management Organizations with analysis and planning; and we implement projects with willing landowners to improve water quality and habitat in the river. ACD is also involved with guiding land conservation projects near the Rum River needed to protect habitat and water quality, and we are working diligently with other local organizations to ensure future funding for projects protecting the Rum River.
Over the coming months, we will be posting short blogs to highlight individual projects and programs that ACD has directed for the benefit of the Rum River. Check in soon at www.anokaswcd.org/blog to learn more!