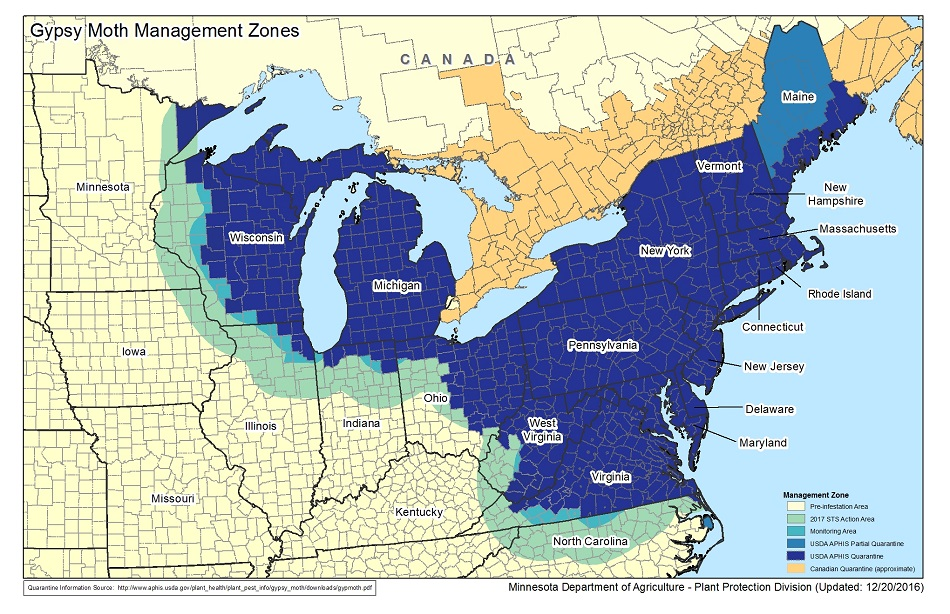
Minnesota's Noxious Weed Law is the policy of the legislature that residents of the state be protected from the injurious effects that noxious weeds have on public health, environment, public roads, crops, livestock, and other property. A noxious weed is a regulated plant species that has been designated as one of the four categories; Prohibited Eradicate, Prohibited Control, Restricted, and Specially Regulated.
The Prohibited Eradicate category include species that are highly damaging with limited distribution. These species are listed with the goal of eradication. Some examples found in Minnesota include Black Swallow-wort, Oriental Bittersweet, and the Tree of Heaven.
The Prohibited Control category include species that are highly damaging and widely distributed. The goal for species in this category is to prevent spreading. Examples in Minnesota include Wild Parsnip, Common Tansy, and Japanese Knotweed.
The Restricted Category include species that are highly damaging with an extensive distribution that limits the ability to control populations. The goal for these species is to prevent new plantings. Examples in Minnesota include Common Buckthorn, Non-Native Honeysuckle, and Garlic Mustard.
Specially Regulated plants may be native, non-native, or demonstrated value. The goal for this category of plants is to craft regulations that prevent issues. Examples in Minnesota include Poison Ivy, Amur Maple, and Winged Burning Bush.
Species on this list and new potential treats are reviewed by the Noxious Weed Advisory Committee. This committee is comprised of members that represent conservation, business, tribes, and government interests. A thorough risk assessment is completed for a species before a listing recommendation is made by the committee. You can report a potential population of a species on the Minnesota Noxious Weed List by taking a picture of both the leaves and flowers, taking note of the location, and sending it to the Arrest the Pest email This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. or by filing out the online reporting form on the website https://mdaonbase.mda.state.mn.us/AppNetUF/UnityForm.aspx?key=UFKey.
Below is a list of species to keep a look out for. Some of these species are already listed as Prohibited Eradicate in Minnesota and have very limited distribution. Looking for these species can prevent new populations from invading the state. Other species on the list have not yet been found in Minnesota, but have caused substantial damage in other parts of the country. Early detection and eradication is crucial in protecting Minnesota against invasive species.