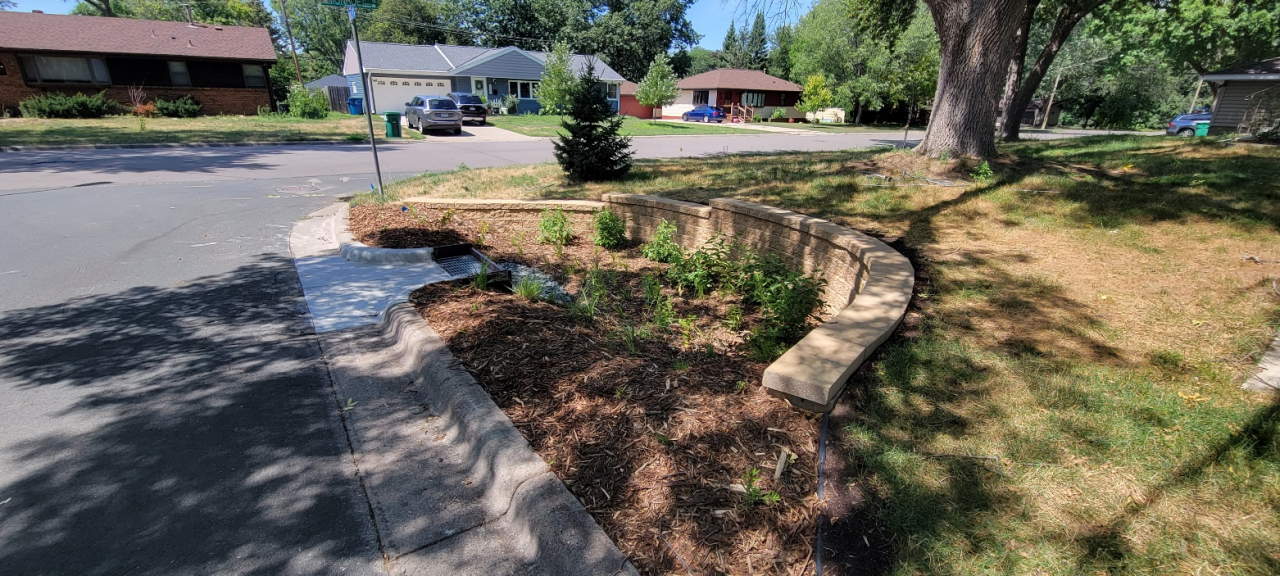
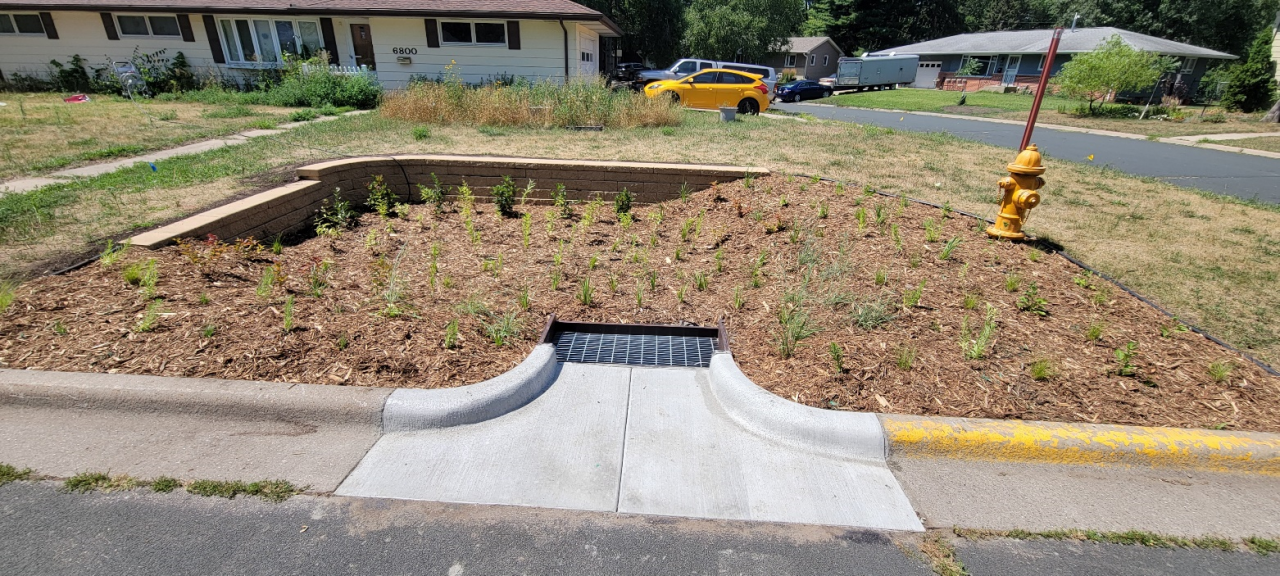
As summer warms up, the likelihood of harmful algae blooms increases. Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, are a type of photosynthetic bacteria. Cyanobacteria are naturally found in all lakes, rivers, and ponds, and, like plants and algae, they perform photosynthesis, obtaining their energy from the sun. Unlike true algae, cyanobacteria aren't a key part of the food chain, and most organisms choose not to eat them. Under the right circumstances, cyanobacteria can multiply to form a bloom. A bloom is a sudden increase in cyanobacterial cells in a specific area of water. Some species of cyanobacteria can create toxins that are harmful to human and animal health, known as cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms (cyanoHABs).
CyanoHABs can make people and animals sick if they breathe in, swallow, or come into contact with water or scum that contains toxins. Sunlight, high temperatures, and abundant nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, can increase the likelihood of a bloom occurring. Warm weather patterns and significant rain events that result in more stormwater runoff entering the water can also jump-start a bloom. Blooms typically occur during the warmer months, between mid-June and mid-September. As Minnesota's climate changes, it's fueling more frequent and intense rain events, floods, and warmer weather, contributing to more harmful algal blooms. For more information, check out the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency webpage or contact Kris Larson, Water Resource Specialist, at