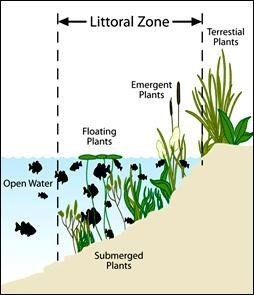
Emergent Vegetation Plays an Important Role in Lake Health
Emergent aquatic plants such as cattails, bulrushes, and sedges grow within the shallow margins, or "littoral zone", of most lakes in Minnesota. These plants improve water clarity as their roots stabilize the lakebed and take in nutrients. Their stems and leaves provide habitat both above and below the water, and they protect shorelines against the forces of wave action. Emergent plants often grow alongside other aquatic vegetation, collectively creating diverse habitat essential to lake health.
Any Destruction of Emergent Vegetation Requires a Permit in Minnesota - Lakeshore owners often wish to remove emergent vegetation to improve their water access. Given the important role emergent vegetation plays in lakes, any removal of aquatic emergent plants requires a permit from the Department of Natural Resources. The permit process connects landowners with professionals to ensure that the extent of vegetation removal (and methods used to achieve it) minimize impacts to the lake. Learn more about aquatic plant regulations HERE.
When Does Emergent Vegetation Become Problematic? - Non-native species such as narrow-leaf and hybrid cattails often grow in dense monocultures that can outcompete native species. Habitat quality and recreation can be quickly reduced as these species spread across large areas of shallow water, but management efforts to remove them are often challenging and costly. When occurring in small clusters, these plants can still provide water quality benefits along shorelines where native emergent plants are absent. In either circumstance, any removal of emergent plants - even if non-native - requires a permit.
Expectations for Living on a Lake - Aquatic vegetation is a natural and important part of lake and wetland systems. The abundance and types of plants present are largely driven by water depth and clarity. Many lakes in the north metro are shallow (less than 15 ft. deep) or are technically open-water wetlands. When paired with good water quality allowing sunlight to reach the bottom, these lakes usually contain abundant vegetation throughout. The alternative is poor water quality from disturbances such as excessive nutrients, which can reduce aquatic vegetation and the fish and wildlife that depend on it. Learn more about shallow lake vegetation from this StoryMap produced by the Rice Creek Watershed District: Aquatic Plants: Guardians of our Shallow Lakes.
For more information contact Breanna Keith, Water Resource Specialist, at
When you subscribe to the blog, we will send you an e-mail when there are new updates on the site so you wouldn't miss them.