It is time to think about SPRING! ACD is taking pre-orders for the annual tree and shrub sale. Pickup is on the last Saturday in April.
• Order early to guarantee availability
• Over 25+ species available
• You do not need to be an Anoka County Resident to order.
• All trees and shrubs are sold as bare-root seedlings.
• Most are sold in bundles of ten for $24 or twenty-five for $46 - not including tax.
• Native prairie seed and tree aides are also available.
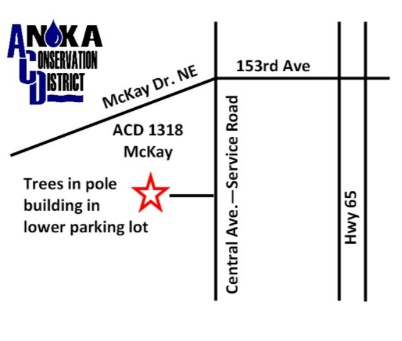
• PICK UP LOCATION -Anoka Conservation District - in Pole Building (lower lot)
Pick up details announced at the beginning of April 2026 (typically the last Saturday in April).
Order online today or contact Kathy Berkness, Office Administrator, at
ACD wraps up another successful annual tree sale! Over 26,000 trees were purchased as bare-root seedlings in bundles of ten or twenty-five. We offered a variety of species including black cherry, mixed oak, maple, lilac, pine trees, and a variety of native prairie seed mixes. We had perfect weather on pick-up day and our staff enjoyed getting the chance to meet and engage with the 466 tree sale customers. Thank you to everyone who purchased trees and helped support local conservation efforts! Check out a recap of our 2025 Tree Sale below!
ACD's tree sale is right around the corner! Trees and shrubs are sold in bareroot seedlings or transplants, ranging from 8" to 18" in height. They may be purchased in bundles of ten for $24.00, or twenty-five for $47 not including tax. Native prairie seed and tree aides are also available. You do not need to be an Anoka County Resident to order. The order form is organized to group native trees and shrubs according to their ecosystem and non-native trees and shrubs based upon their primary use. Call 763-434-2030 x 100 or email
You may have observed a major difference between this year and our last few growing seasons: plenty of precipitation. According to the DNR's Climatology Office, the amount of rain that's fallen from April through August 2024 has been nearly the most on record over a good share of Minnesota. Overall, this is good news for our forests – but all that near- historic rainfall has had additional impacts to trees.
As shoots and leaves emerge in the spring, they're particularly susceptible to infection from fungal pathogens. Extremely wet weather during this timeframe promotes sporulation (formation of spores) of these microscopic fungi, and rain spreads the spores around. The end result is a slew of common leaf diseases that we've seen in 2024.
Read the full article from the MNDNR or contact Becky Wozney, Wetland Specialist, at
Addressing eroding slopes along an undeveloped portion of the Martin Lake shoreline required a creative stabilization solution. Sandy soils, wave action (increasing with boat activity), and fluctuating water levels cumulatively drove soil loading to the lake and the gradual encroachment of the shoreline toward the adjacent road. However, site access and workable land upslope was limited, and preserving mature trees and other natural shoreline elements was a priority. To achieve this, sections of stacked logs were anchored to the base of the shoreline along critical eroding areas.
The lower logs act as a barrier to prevent waves from washing out soil at the base of the slope, and the upper logs trap the sandy soil falling from behind – rebuilding the eroded voids and creating a more stable slope within which vegetation can become re-established. At the same time, wildlife such as nesting turtles can still access these areas. ACD staff will continue monitoring this site in the coming years to assess its long-term effectiveness in protecting the shoreline. For more information contact Breanna Keith,Water Resource Specialist, at
ACD is now taking orders for the 2024 tree sale! The district offers a variety of species including black cherry, mixed oak, maple, lilac and pine trees. Trees can be purchased as bare root seedlings in bundles of ten for $23.00, or twenty-five for $45.00, not including tax. Mixes of native prairie seed are also available. You do not need to be an Anoka County resident to order. Click here to learn more and place your order today! For more information contact Kathy Berkness, Office Administrator,
ACD is going to start taking tree orders in mid-October for an end of April pick up. The trees and shrubs are sold as bare root seedlings or transplants ranging from 12" to 18" in height. They may be purchased in bundles of ten for $20 or twenty-five for $40, not including tax. Native prairie seed and tree aides are also available.
You do not need to be an Anoka County Resident to order.
Call 763-434-2030 x 100 or email
Pre-ordered trees & shrubs will be ready for pick up on April 30th, staggered by last name.
DATE AND TIME: Saturday, April 30. Staggered pick up by first letter of Last Name:
A-D: 9-9:30am P-S: 11:15-11:45am
E-J: 9:45-10:15am T-Z: 12-12:30pm
K-O: 10:30-11am
PICK UP LOCATION: ACD Office- 1318 McKay Drive NE Ham Lake LOWER LOT
- We strongly encourage you to come during your timeslot
- Drive-thru pick up to comply with social distancing
- Make space ahead of time so ACD staff can put your order in your vehicle
- Refer to www.AnokaSWCD.org for up-to-date information
- Ask a neighbor or friend to pick up if you can't make it
- Parking lot is too small, so no large trailers!!
Storing your seedlings until they can be planted:
- Store trees and shrubs in a cool, dark location (garage or shed)
- Your trees and shrubs should be fine stored for up to 3 weeks
- Keep roots moist but don't fill bag with water or put roots in a bucket of water
- Roots have been dipped in root gel and bagged to keep them moist
Questions?
1st, try: www.AnokaSWCD.org
2nd, email:
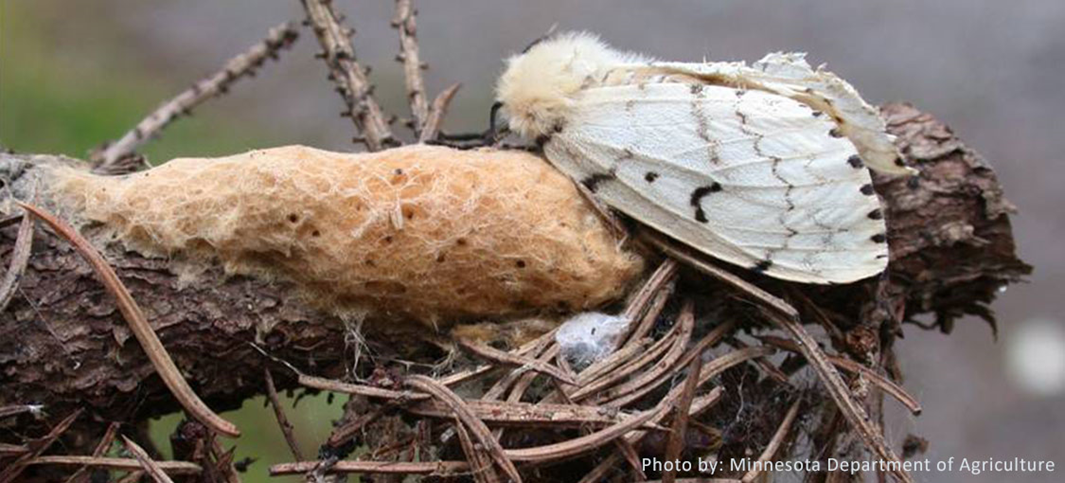
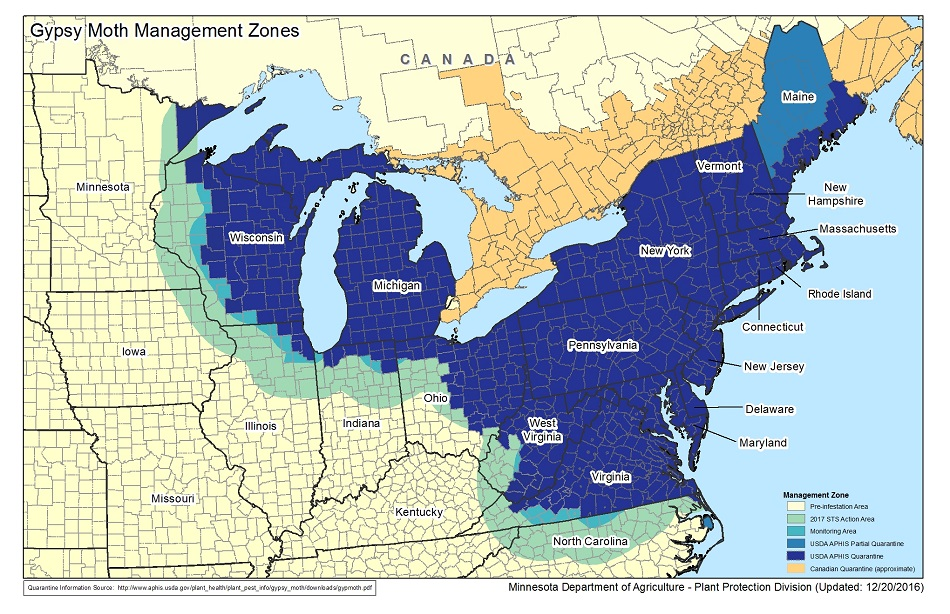
Lymantria Dispar is an invasive moth formerly known by the common name Gypsy Moth. Last year, the Entomological Society of America officially changed the common name for this invasive species to the Spongy Moth. Romani people, Europe's largest ethnic group, generally consider the common name "Gypsy Moth" to contain a racial slur. The Entomological Society of America states that "while the use of an ethnic slur is enough reason to stop using a common name, the former common name was doubly inappropriate in that it linked a group of people who have been treated as pests and the targets of genocide with an invasive pest insect that remains targeted for population control and eradication, all of which combined to have dehumanizing effects for Romani people."
The new common name for Lymantria Dispar, the spongy moth, refers to the insect's light brown, fuzzy egg masses. This new name also aligns better with other countries common name for this invasive species. This moth is known for defoliating deciduous forests while in their caterpillar form. This repeated defoliation causes stress and can leave trees vulnerable to other diseases and pests. Spongy moths were introduced to the United States from Europe in the nineteenth century. They have spread from their initial location in Massachusetts westward, in both the United States and Canada.
Since 2004, Minnesota has been a member of the U.S. Forest Service's Slow the Spread (STS) program. Cook and Lake Counties are the only places with reproducing spongy moths in Minnesota. Parts of Eastern Minnesota are within the transition zone, and most of the state is still listed as an uninfested zone. Currently, Anoka County is still within the uninfested zone, but the spread of the spongy moth is occurring at a rate of 3 miles per year.
By far the most frequently asked question as part of our annual tree sale is "how fast will this tree grow?" Simple enough, yet so complicated.
It would be great if we could say "one to two feet per year." That's what customers want to hear. Five feet per year is even better. The truth is more nuanced. A 'slow growing' tree planted in just the right place can easily outgrow a 'fast growing' tree that is planted in the wrong place. Trees can be finicky about how sunny they like it, how wet they want it, how nutrient rich they need it, how cold they can tolerate, or how salty they will bear.
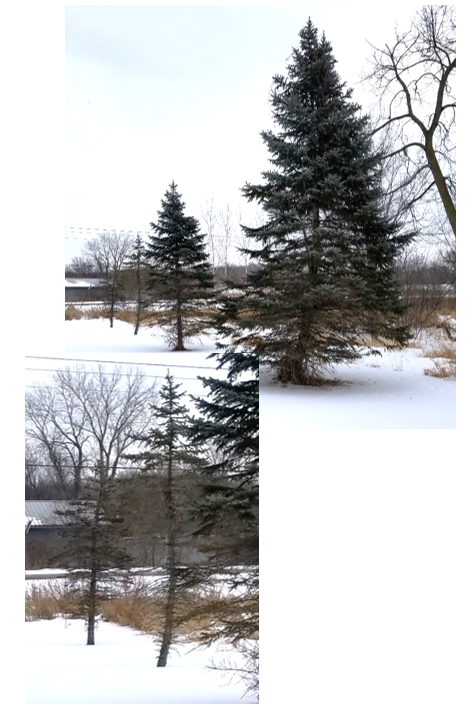
For example, spruce trees like sunny spots that aren't too wet. Never a very fast growing tree to begin with, if put in the wrong place, they can grow painfully slow. In the photos,15 years ago four 3-foot tall potted Colorado Blue Spruce trees were planted in a row about 25 feet apart. The closest tree in the photo is about 25 feet tall and fairly full. The next is 15 feet tall and not looking too bad. The third is a scraggly 12 feet tall. The fourth is clinging to life and tops out at around 9 feet tall.
All four trees have enough sunlight so that isn't the problem. The best grower is planted in ground that is sandier and about 2 feet higher in elevation than the saddest of the bunch, which is planted in a peaty soil that was once a wetland. From the best to the worst grower, they are planted in progressively wetter areas. The fastest grew 18 inches per year while the slowest grew only 4 inches per year.
This is why when asked "how fast will my tree grow?" we hesitate and then follow with "it depends…" This is also why we include all the information you need to select the right tree for your property as part of our sale. Choose well and your trees will flourish, and if you need a little help, give us a call.
The Anoka Conservation is currently taking tree orders for the district's annual sale taking place at the end of April, 2022. Trees and shrubs are sold as bare root seedlings or transplants and can range from 8" to 24" in height. Species may be purchased in bundles of ten for $19.00, or twenty-five for $38 (tax not included). Native prairie seed and tree aides are also available. Order today as supply is running out! You do not need to be an Anoka County resident to order. Call 763-434-2030 x100 or email
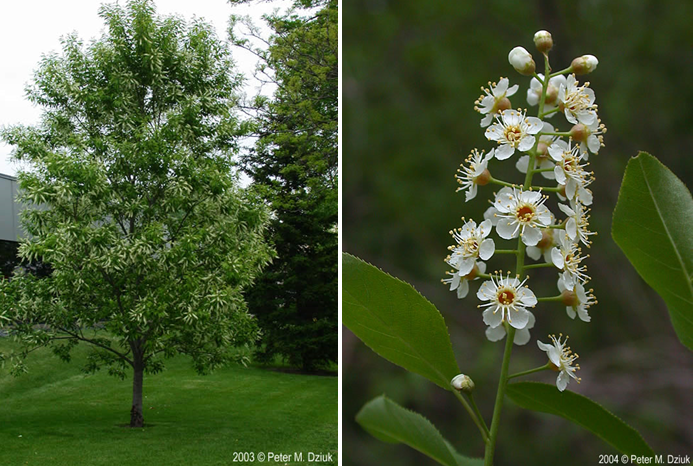
If you are looking for a low maintenance option to benefit native pollinators, consider planting native trees and shrubs. They provide overwintering habitat and food sources for our native bees, butterflies, moths, flies, wasps, and beetles. Many trees and shrubs bloom in the spring and provide an early nectar and pollen source. Fun fact from Heather Holm: One, 70 foot tall, mature black cherry tree (photos below) has the equivalent number of flowers as a 3,500 square foot perennial garden.
ACD's Annual Tree sale has a wide variety of trees and shrubs to choose from! See the full catalog here: https://www.anokaswcd.org/tree-sale-order-forms/2012-10-26-17-32-43.html
See Heather Holm's Native Tree and Shrubs for Pollinators guide for more information: https://www.pollinatorsnativeplants.com/uploads/1/3/9/1/13913231/treesshrubsposter.pdf
Climate change has many impacts on the natural environment and there are many ways we can help reduce climate change. There is yet another way to help with the impacts of climate change. Planting a diversity of trees that are predicted to thrive in a changing climate will help the landscape adapt and become more resilient.
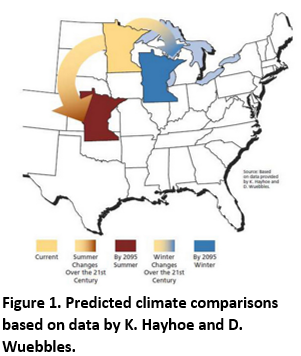
Minnesota's climate is changing. Average temperatures have increased 1 - 3 ◦F statewide with the greatest temperature increases in the winter. Total precipitation has increased with more intense rainfalls. Despite the increase in total precipitation, there have been more days between precipitation events, which increases the potential for drought. The US National Climate Assessment predicts that these trends will continue in Minnesota. By the end of the century, Minnesota will likely have the summer climate of Nebraska and Kansas (Figure 1). Plant communities and habitat types will change along with the changing climate. Most tree species northward range are predicted to shift about 300 miles by the end of the century (McKenney et al. 2007). The change in tree cover alters the understory and the habitat for wildlife. One way to help the landscape adapt and become more resilient is to plant a diversity of trees and include species from more southern areas.
US Forest Service climate change models predict these trees are likely to thrive in a changing climate in the Metro region:
| Tree Species | Habitat |
| American elm * | Average – Moist soil, floodplains, deciduous forest, swamps |
| Basswood | Deciduous forests, woodland edges |
| Black Oak | Savanna |
| Black Walnut | Mixed forest, Savannas, banks |
| Bur Oak | Forest to open prairie |
| Cottonwood | Lowland forests along along lakes and streams, floodplains |
| Hackberry | Average – Moist soil, Hardwood forest, floodplains, river bank |
| Shagbark hickory | Upland dry forest |
| Silver maple | Floodplain forest, riverbanks |
| White Oak | Upland dry forest |
| * disease resistant needed Consider the habitat, moisture, soil, and sun conditions when selecting trees for your property. | |
https://www.dnr.state.mn.us/treecare/best-native-yard-trees.html
McKenney DW Pedlar JH Lawrence K Campbell K Hutchinson MF. 2007. Potential impacts of climate change on the distribution of North American trees. BioScience 57:939-948.