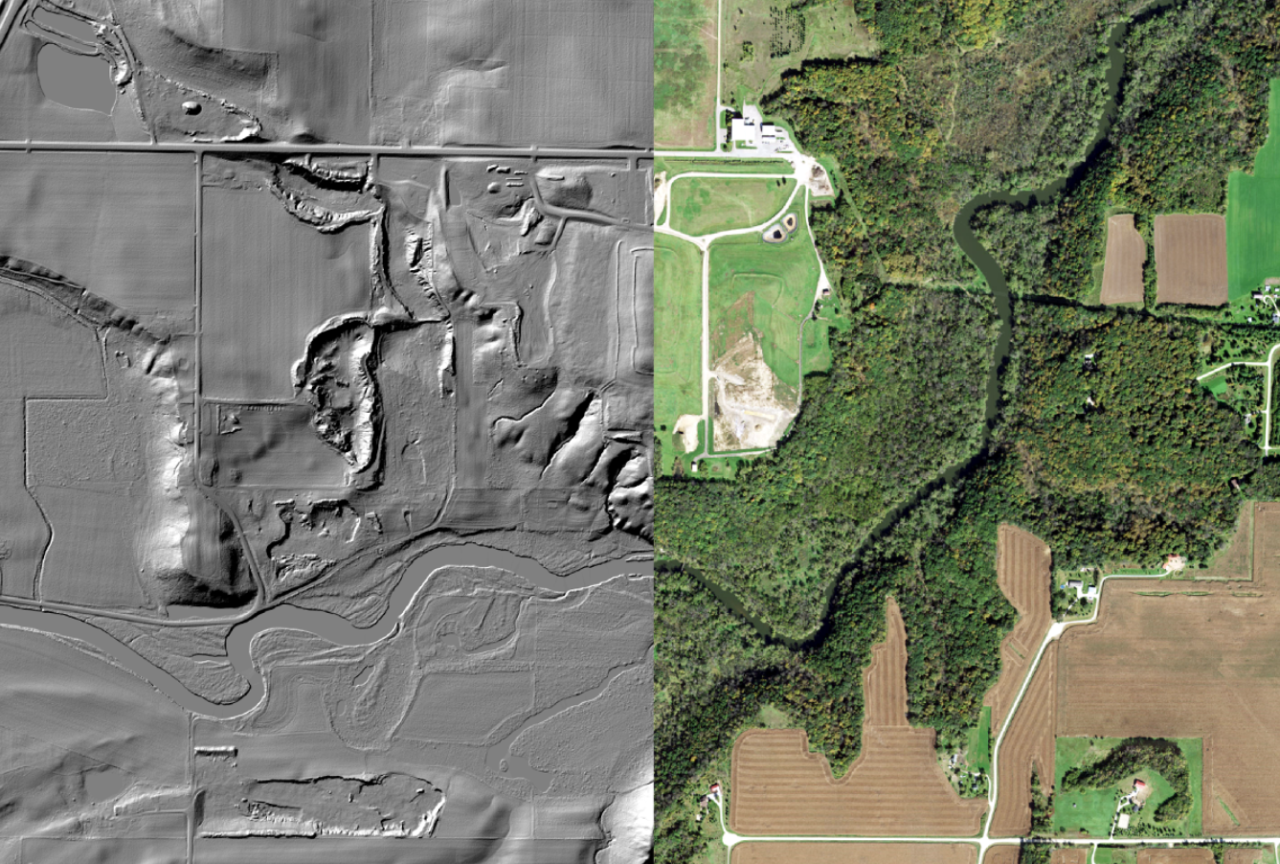
Minnesota Gets New LiDAR Data
LiDAR stands for Light Detection and Ranging. The landscape is mapped by laser pulses projected from a low-flying airplane. These pulses bounce back to a sensor which records the location of the airplane, the angle of the pulse, and the time it takes the light to bounce back. Using that information, the system is able to create a point cloud of the landscape. This point cloud is then converted into modeled surface of the ground called a Digital Elevation Model (DEM). This model can be used to map terrain features like water flow paths and drainage areas, geologic features, infrastructure, and many others.
The first generation of LiDAR data in Minnesota was collected from 2008-2012. Since then, the landscape has changed in untold ways, and technology has dramatically improved for collecting more dense and accurate data. Because of this, the 3D Geomatics Committee of the State's Geospatial Advisory Council set out to coordinate the collection of Generation 2 LiDAR in Minnesota. This effort is currently underway in partnership with the USGS as the lead data collection entity nationally, and counties and other local partners as the ultimate data recipients. Generation 2 LiDAR data collection started in 2021. Anoka County data was collected in 2022, and will be available in 2023.
This new data will allow us to map watercourses, drainage areas, and floodways in much higher resolution and with more accurate and recent data from the landscape. We'll also be able to assess eroding slopes like those along riverbanks for height, steepness, and stability without having to traverse them with survey gear. Because the new data is so robust, it is also opening up possibilities for forestry and vegetation surveys, very detailed mapping of infrastructure, and untold uses yet to be implemented or even thought of.
For more information about this incredibly useful public data, visit the Minnesota LiDAR Hub online at: https://lidarhub-minnesota.hub.arcgis.com/